Multifaceted Interweaving Between Extracellular Matrix, Insulin Resistance, and Skeletal Muscle
- PMID: 30249008
- PMCID: PMC6211053
- DOI: 10.3390/cells7100148
Multifaceted Interweaving Between Extracellular Matrix, Insulin Resistance, and Skeletal Muscle
Abstract
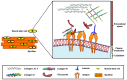
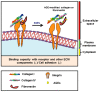
The skeletal muscle provides movement and support to the skeleton, controls body temperature, and regulates the glucose level within the body. This is the core tissue of insulin-mediated glucose uptake via glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4). The extracellular matrix (ECM) provides integrity and biochemical signals and plays an important role in myogenesis. In addition, it undergoes remodeling upon injury and/or repair, which is also related to insulin resistance (IR), a major cause of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Altered signaling of integrin and ECM remodeling in diet-induced obesity is associated with IR. This review highlights the interweaving relationship between the ECM, IR, and skeletal muscle. In addition, the importance of the ECM in muscle integrity as well as cellular functions is explored. IR and skeletal muscle ECM remodeling has been discussed in clinical and nonclinical aspects. Furthermore, this review considers the role of ECM glycation and its effects on skeletal muscle homeostasis, concentrating on advanced glycation end products (AGEs) as an important risk factor for the development of IR. Understanding this complex interplay between the ECM, muscle, and IR may improve knowledge and help develop new ideas for novel therapeutics for several IR-associated myopathies and diabetes.
Keywords: advanced glycation end products; extracellular matrix; insulin resistance; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources