Molecular Mechanisms of H. pylori-Induced DNA Double-Strand Breaks
- PMID: 30249046
- PMCID: PMC6213211
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19102891
Molecular Mechanisms of H. pylori-Induced DNA Double-Strand Breaks
Abstract
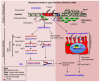
Infections contribute to carcinogenesis through inflammation-related mechanisms. H. pylori infection is a significant risk factor for gastric carcinogenesis. However, the molecular mechanism by which H. pylori infection contributes to carcinogenesis has not been fully elucidated. H. pylori-associated chronic inflammation is linked to genomic instability via reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS). In this article, we summarize the current knowledge of H. pylori-induced double strand breaks (DSBs). Furthermore, we provide mechanistic insight into how processing of oxidative DNA damage via base excision repair (BER) leads to DSBs. We review recent studies on how H. pylori infection triggers NF-κB/inducible NO synthase (iNOS) versus NF-κB/nucleotide excision repair (NER) axis-mediated DSBs to drive genomic instability. This review discusses current research findings that are related to mechanisms of DSBs and repair during H. pylori infection.
Keywords: BER; DSBs; H. pylori; NER; NF-κB; RONS.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
H. pylori-Induced DNA Strand Breaks Are Introduced by Nucleotide Excision Repair Endonucleases and Promote NF-κB Target Gene Expression.Cell Rep. 2015 Oct 6;13(1):70-79. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.08.074. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26411687
-
Genetic battle between Helicobacter pylori and humans. The mechanism underlying homologous recombination in bacteria, which can infect human cells.Microbes Infect. 2014 Oct;16(10):833-9. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2014.08.001. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Microbes Infect. 2014. PMID: 25130723 Review.
-
A lucid review of Helicobacter pylori-induced DNA damage in gastric cancer.Helicobacter. 2019 Oct;24(5):e12631. doi: 10.1111/hel.12631. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Helicobacter. 2019. PMID: 31295756 Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori-Mediated Genetic Instability and Gastric Carcinogenesis.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;400:305-323. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50520-6_13. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28124159 Review.
-
Accumulation of abasic sites induces genomic instability in normal human gastric epithelial cells during Helicobacter pylori infection.Oncogenesis. 2014 Nov 24;3(11):e128. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2014.42. Oncogenesis. 2014. PMID: 25417725 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immunological Perspective: Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Mar 8;2022:2944156. doi: 10.1155/2022/2944156. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 35300405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Gastric Microorganisms Other than Helicobacter pylori in the Development and Treatment of Gastric Diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Mar 14;2022:6263423. doi: 10.1155/2022/6263423. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35321071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Features Distinguish Gastric Cancer Subtypes.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 11;19(10):3121. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103121. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30314372 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Gut Microbiota Balance on the Health-Disease Relationship: The Importance of Consuming Probiotics and Prebiotics.Foods. 2021 Jun 2;10(6):1261. doi: 10.3390/foods10061261. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34199351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbiome in cancer: An exploration of carcinogenesis, immune responses and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 8;13:877939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.877939. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36003378 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

