Musculoskeletal conditions may increase the risk of chronic disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies
- PMID: 30249247
- PMCID: PMC6154805
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-018-1151-2
Musculoskeletal conditions may increase the risk of chronic disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies
Abstract
Background: Chronic diseases and musculoskeletal conditions have a significant global burden and frequently co-occur. Musculoskeletal conditions may contribute to the development of chronic disease; however, this has not been systematically synthesised. We aimed to investigate whether the most common musculoskeletal conditions, namely neck or back pain or osteoarthritis of the knee or hip, contribute to the development of chronic disease.
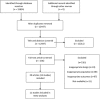
Methods: We searched CINAHL, Embase, Medline, Medline in Process, PsycINFO, Scopus and Web of Science to February 8, 2018, for cohort studies reporting adjusted estimates of the association between baseline musculoskeletal conditions (neck or back pain or osteoarthritis of the knee or hip) and subsequent diagnosis of a chronic disease (cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, chronic respiratory disease or obesity). Two independent reviewers performed data extraction and assessed study quality. Adjusted hazard ratios were pooled using the generic inverse variance method in random effect models, regardless of the type of musculoskeletal condition or chronic disease.
Prospero: CRD42016039519.
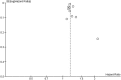
Results: There were 13 cohort studies following 3,086,612 people. In the primary meta-analysis of adjusted estimates, osteoarthritis (n = 8 studies) and back pain (n = 2) were the exposures and cardiovascular disease (n = 8), cancer (n = 1) and diabetes (n = 1) were the outcomes. Pooled adjusted estimates from these 10 studies showed that people with a musculoskeletal condition have a 17% increase in the rate of developing a chronic disease compared to people without (hazard ratio 1.17, 95% confidence interval 1.13-1.22; I2 52%, total n = 2,686,113 people).
Conclusions: This meta-analysis found that musculoskeletal conditions may increase the risk of chronic disease. In particular, osteoarthritis appears to increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Prevention and early treatment of musculoskeletal conditions and targeting associated chronic disease risk factors in people with long standing musculoskeletal conditions may play a role in preventing other chronic diseases. However, a greater understanding about why musculoskeletal conditions may increase the risk of chronic disease is needed.
Keywords: Back pain; Chronic disease; Meta-analysis; Osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Feigin V. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 315 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE), 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1603–1658. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30679-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014: attaining the nine global noncommunicable diseases targets. Geneva: WHO; 2014.
-
- Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1545–1602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

