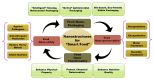
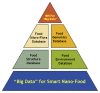
Prospects of using nanotechnology for food preservation, safety, and security
- PMID: 30249319
- PMCID: PMC9298566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.06.011
Prospects of using nanotechnology for food preservation, safety, and security
Abstract
The rapid development of nanotechnology has transformed many domains of food science, especially those that involve the processing, packaging, storage, transportation, functionality, and other safety aspects of food. A wide range of nanostructured materials (NSMs), from inorganic metal, metal oxides, and their nanocomposites to nano-organic materials with bioactive agents, has been applied to the food industry. Despite the huge benefits nanotechnology has to offer, there are emerging concerns regarding the use of nanotechnology, as the accumulation of NSMs in human bodies and in the environment can cause several health and safety hazards. Therefore, safety and health concerns as well as regulatory policies must be considered while manufacturing, processing, intelligently and actively packaging, and consuming nano-processed food products. This review aims to provide a basic understanding regarding the applications of nanotechnology in the food packaging and processing industries and to identify the future prospects and potential risks associated with the use of NSMs.
Keywords: Food preservation; Food safety; Functional food; Human health; Nanostructured materials (NSMs); Packaging.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Chandra P.Nanobiosensors for personalized and onsite biomedical diagnosis. The Institution of Engineering and Technology. 2016. - DOI
-
- Sandoval B. Perspectives on FDA's regulation of nanotechnology: emerging challenges and potential solutions. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2009;8:375–93.
-
- Moriarty P. Nanostructured materials. Rep Prog Phys. 2001;64:297.
-
- Bhushan B. Springer handbook of nanotechnology. Berlin; Heidelberg: Springer Science & Business Media; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources