Diagnostic value of combined serum biomarkers for the evaluation of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C infection: A multicenter, noninterventional, observational study
- PMID: 30249562
- PMCID: PMC6284637
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2018.16597
Diagnostic value of combined serum biomarkers for the evaluation of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C infection: A multicenter, noninterventional, observational study
Abstract
Background/aims: The hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is important cause of chronic hepatitis. Liver biopsy is considered the gold standard for assessment of fibrosis but this procedure is an invasive procedure. We aimed to evaluate the diagnostic efficiency of non-invasive serum biomarkers, separately and in combinations, on liver fibrosis in treatment-naive chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients.
Materials and methods: Two hundred and sixteen treatment-naive CHC patients were enrolled from 32 locations across Turkey in this open-labelled, non-interventional prospective observational study. FibroTest®, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index(APRI), aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase ratio (AAR), fibrosis index based on four factors (FIB-4), Age-platelet(AP) index and Forns index were measured and compared with Metavir scores got from liver biopsies.
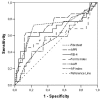
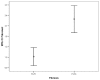
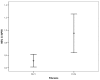
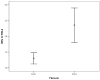
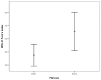
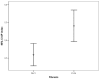
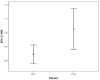
Results: Data from 182 patients with baseline liver biopsy were suitable for analysis. One hundred and twenty patients (65.9%) had F0-F1 fibrosis and 62 patients (34.1%) had F2-F4 fibrosis. APRI 0.732 area under the curve(AUC) indicated advanced fibrosis with 69% sensitivity and 77% specificity. FIB-4 0.732 AUC and FibroTest 0.715 AUC indicated advanced fibrosis with 69% and 78.4% sensitivity, and 75% and 71.4% specificity, respectively. The combined use of tests also led to an increase in AUC and specificity. Combinations of FibroTest with APRI and/or FIB-4, and FIB-4 with APRI were optimal for the evaluation of liver fibrosis.
Conclusion: Fibrotest, FIB-4, APRI, AP index and Forns index exhibit good diagnostic performance for determining liver fibrosis in CHC patients, and the use of at least two tests together will increase their diagnostic value still further.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Serum biomarkers for the evaluation of liver fibrosis: The need for better tests.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul;29(4):377-378. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2018.260618. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30249549 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Fibrosis index based on four factors better predicts advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis than aspartate aminotransferase/platelet ratio index in chronic hepatitis C patients.J Formos Med Assoc. 2015 Oct;114(10):923-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2015.07.004. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Formos Med Assoc. 2015. PMID: 26279173
-
AST-platelet ratio index, Forns index and FIB-4 in the prediction of significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jun;22(3):279-85. doi: 10.4318/tjg.2011.0213. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21805418
-
The PAPAS index: a novel index for the prediction of hepatitis C-related fibrosis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Aug;27(8):895-900. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000379. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25951491
-
APRI test and hyaluronic acid as non-invasive diagnostic tools for post HCV liver fibrosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Arab J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jun;18(2):51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ajg.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28579340
-
Staging liver fibrosis and cirrhosis using non-invasive tests in people with chronic hepatitis B to inform WHO 2024 guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Apr;10(4):332-349. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(24)00437-0. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39983746
Cited by
-
Hepatic Steatosis Predicts Higher Incidence of Recurrence in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Patients.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 9;11:631943. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.631943. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33767997 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated neural network and evolutionary algorithm approach for liver fibrosis staging: Can artificial intelligence reduce patient costs?JGH Open. 2024 May 9;8(5):e13075. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.13075. eCollection 2024 May. JGH Open. 2024. PMID: 38725944 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical application of deep learning and radiomics in hepatic disease imaging: a systematic scoping review.Br J Radiol. 2022 Aug 1;95(1136):20211136. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20211136. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Br J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35816550 Free PMC article.
-
Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI): A potential marker for diagnosis in patients at risk of severe malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 25;14(11):e0224877. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224877. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31765438 Free PMC article.
-
Application of artificial intelligence in chronic liver diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Jan 6;21(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01585-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33407169 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
