Web-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Blended With Face-to-Face Sessions for Major Depression: Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 30249583
- PMCID: PMC6231848
- DOI: 10.2196/10743
Web-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Blended With Face-to-Face Sessions for Major Depression: Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Meta-analyses of several randomized controlled trials have shown that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has comparable efficacy to antidepressant medication, but therapist availability and cost-effectiveness is a problem.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of Web-based CBT blended with face-to-face sessions that reduce therapist time in patients with major depression who were unresponsive to antidepressant medications.
Methods: A 12-week, assessor-masked, parallel-group, waiting- list controlled, randomized trial was conducted at 3 medical institutions in Tokyo. Outpatients aged 20-65 years with a primary diagnosis of major depression who were taking ≥1 antidepressant medications at an adequate dose for ≥6 weeks and had a 17-item GRID-Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD) score of ≥14 were randomly assigned (1:1) to blended CBT or waiting-list groups using a computer allocation system, stratified by the study site with the minimization method, to balance age and baseline GRID-HAMD score. The CBT intervention was given in a combined format, comprising a Web-based program and 12 45-minute face-to-face sessions. Thus, across 12 weeks, a participant could receive up to 540 minutes of contact with a therapist, which is approximately two-thirds of the therapist contact time provided in the conventional CBT protocol, which typically provides 16 50-minute sessions. The primary outcome was the alleviation of depressive symptoms, as measured by a change in the total GRID-HAMD score from baseline (at randomization) to posttreatment (at 12 weeks). Moreover, in an exploratory analysis, we investigated whether the expected positive effects of the intervention were sustained during follow-up, 3 months after the posttreatment assessment. Analyses were performed on an intention-to-treat basis, and the primary outcome was analyzed using a mixed-effects model for repeated measures.
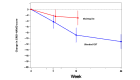
Results: We randomized 40 participants to either blended CBT (n=20) or waiting-list (n=20) groups. All patients completed the 12-week treatment protocol and were included in the intention-to-treat analyses. Participants in the blended CBT group had significantly alleviated depressive symptoms at week 12, as shown by greater least squares mean changes in the GRID-HAMD score, than those in the waiting list group (-8.9 points vs -3.0 points; mean between-group difference=-5.95; 95% CI -9.53 to -2.37; P<.001). The follow-up effects within the blended CBT group, as measured by the GRID-HAMD score, were sustained at the 3-month follow-up (week 24) and posttreatment (week 12): posttreatment, 9.4 (SD 5.2), versus follow-up, 7.2 (SD 5.7); P=.009.
Conclusions: Although our findings warrant confirmation in larger and longer term studies with active controls, these suggest that a combined form of CBT is effective in reducing depressive symptoms in patients with major depression who are unresponsive to antidepressant medications.
Trial registration: University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trials Registry: UMIN000009242; https://upload.umin.ac.jp/cgi-open-bin/ctr_e/ctr_view.cgi?recptno=R000010852 (Archived by WebCite at http://www.webcitation. org/729VkpyYL).
Keywords: blended cognitive behavioral therapy; cognitive behavioral therapy; major depression; major depressive disorder; randomized controlled trial.
©Shigetsugu Nakao, Atsuo Nakagawa, Yoshiyo Oguchi, Dai Mitsuda, Noriko Kato, Yuko Nakagawa, Noriko Tamura, Yuka Kudo, Takayuki Abe, Mitsunori Hiyama, Satoru Iwashita, Yutaka Ono, Masaru Mimura. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 21.09.2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: AN has received royalties from Igaku-Shoin and Kongo-Shuppan publishers. YO is the developer or sponsor of the
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Depression http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs369/en/
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Ackerman I, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Ali MK, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Bahalim AN, Barker-Collo S, Barrero LH, Bartels DH, Basáñez M, Baxter A, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bernabé E, Bhalla K, Bhandari B, Bikbov B, Bin AA, Birbeck G, Black JA, Blencowe H, Blore JD, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Bonaventure A, Boufous S, Bourne R, Boussinesq M, Braithwaite T, Brayne C, Bridgett L, Brooker S, Brooks P, Brugha TS, Bryan-Hancock C, Bucello C, Buchbinder R, Buckle G, Budke CM, Burch M, Burney P, Burstein R, Calabria B, Campbell B, Canter CE, Carabin H, Carapetis J, Carmona L, Cella C, Charlson F, Chen H, Cheng AT, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de VKC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahiya M, Dahodwala N, Damsere-Derry J, Danaei G, Davis A, De LD, Degenhardt L, Dellavalle R, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Derrett S, Des JDC, Dharmaratne SD, Dherani M, Diaz-Torne C, Dolk H, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Edmond K, Elbaz A, Ali SE, Erskine H, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ewoigbokhan SE, Farzadfar F, Feigin V, Felson DT, Ferrari A, Ferri CP, Fèvre EM, Finucane MM, Flaxman S, Flood L, Foreman K, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FGR, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabbe BJ, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Ganatra HA, Garcia B, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gmel G, Gonzalez-Medina D, Gosselin R, Grainger R, Grant B, Groeger J, Guillemin F, Gunnell D, Gupta R, Haagsma J, Hagan H, Halasa YA, Hall W, Haring D, Haro JM, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Higashi H, Hill C, Hoen B, Hoffman H, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Huang JJ, Ibeanusi SE, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jarvis D, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Jonas JB, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Kawakami N, Keren A, Khoo J, King CH, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Laden F, Lalloo R, Laslett LL, Lathlean T, Leasher JL, Lee YY, Leigh J, Levinson D, Lim SS, Limb E, Lin JK, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Liu W, Loane M, Ohno SL, Lyons R, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Malekzadeh R, Mallinger L, Manivannan S, Marcenes W, March L, Margolis DJ, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGill N, McGrath J, Medina-Mora ME, Meltzer M, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Meyer A, Miglioli V, Miller M, Miller TR, Mitchell PB, Mock C, Mocumbi AO, Moffitt TE, Mokdad AA, Monasta L, Montico M, Moradi-Lakeh M, Moran A, Morawska L, Mori R, Murdoch ME, Mwaniki MK, Naidoo K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KMV, Nelson PK, Nelson RG, Nevitt MC, Newton CR, Nolte S, Norman P, Norman R, O'Donnell M, O'Hanlon S, Olives C, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Page A, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Patten SB, Pearce N, Padilla RP, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Pesudovs K, Phillips D, Phillips MR, Pierce K, Pion S, Polanczyk GV, Polinder S, Pope CA, Popova S, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Prince M, Pullan RL, Ramaiah KD, Ranganathan D, Razavi H, Regan M, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Richardson K, Rivara FP, Roberts T, Robinson C, De LFR, Ronfani L, Room R, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Saha S, Sampson U, Sanchez-Riera L, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Scott JG, Segui-Gomez M, Shahraz S, Shepard DS, Shin H, Shivakoti R, Singh D, Singh GM, Singh JA, Singleton J, Sleet DA, Sliwa K, Smith E, Smith JL, Stapelberg NJC, Steer A, Steiner T, Stolk WA, Stovner LJ, Sudfeld C, Syed S, Tamburlini G, Tavakkoli M, Taylor HR, Taylor JA, Taylor WJ, Thomas B, Thomson WM, Thurston GD, Tleyjeh IM, Tonelli M, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Tsilimbaris MK, Ubeda C, Undurraga EA, van DWMJ, van OJ, Vavilala MS, Venketasubramanian N, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weatherall DJ, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Weisskopf MG, Weissman MM, White RA, Whiteford H, Wiebe N, Wiersma ST, Wilkinson JD, Williams HC, Williams SRM, Witt E, Wolfe F, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh P, Zaidi AKM, Zheng Z, Zonies D, Lopez AD, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012 Dec 15;380(9859):2197–223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4.S0140-6736(12)61689-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mathers CD, Loncar D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006 Nov;3(11):e442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030442. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0030442 06-PLME-RA-0071R2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cuijpers P, van SA, van OP, Andersson G. Are psychological and pharmacologic interventions equally effective in the treatment of adult depressive disorders? A meta-analysis of comparative studies. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008 Nov;69(11):1675–85; quiz 1839.ej07m04112 - PubMed
-
- Weitz ES, Hollon SD, Twisk J, van SA, Huibers MJH, David D, DeRubeis RJ, Dimidjian S, Dunlop BW, Cristea IA, Faramarzi M, Hegerl U, Jarrett RB, Kheirkhah F, Kennedy SH, Mergl R, Miranda J, Mohr DC, Rush AJ, Segal ZV, Siddique J, Simons AD, Vittengl JR, Cuijpers P. Baseline Depression Severity as Moderator of Depression Outcomes Between Cognitive Behavioral Therapy vs Pharmacotherapy: An Individual Patient Data Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015 Nov;72(11):1102–9. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.1516.2436905 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

