Use of Bioelectronics in the Gastrointestinal Tract
- PMID: 30249600
- PMCID: PMC6719595
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034165
Use of Bioelectronics in the Gastrointestinal Tract
Abstract
Gastrointestinal (GI) motility disorders are major contributing factors to functional GI diseases that account for >40% of patients seen in gastroenterology clinics and affect >20% of the general population. The autonomic and enteric nervous systems and the muscles within the luminal GI tract have key roles in motility. In health, this complex integrated system works seamlessly to transport liquid, solid, and gas through the GI tract. However, major and minor motility disorders occur when these systems fail. Common functional GI motility disorders include dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, functional dyspepsia, gastroparesis, chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction, postoperative ileus, irritable bowel syndrome, functional diarrhea, functional constipation, and fecal incontinence. Although still in its infancy, bioelectronic therapy in the GI tract holds great promise through the targeted stimulation of nerves and muscles.
Copyright © 2019 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
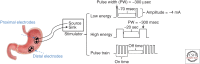
References
-
- Achem SR, Kolts BE, Macmath T, Richter J, Mohr D, Burton L, Castell DO. 1997. Effects of omeprazole versus placebo in treatment of noncardiac chest pain and gastroesophageal reflux. Dig Dis Sci 42: 2138–2145. - PubMed
-
- Allison DB, Fontaine KR, Manson JE, Stevens J, VanItallie TB. 1999. Annual deaths attributable to obesity in the United States. JAMA 282: 1530–1538. - PubMed
-
- Amiot A, Joly F, Alves A, Panis Y, Bouhnik Y, Messing B. 2009. Long-term outcome of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction adult patients requiring home parenteral nutrition. Am J Gastroenterol 104: 1262–1270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
