Functional metagenomics identifies an exosialidase with an inverting catalytic mechanism that defines a new glycoside hydrolase family (GH156)
- PMID: 30249617
- PMCID: PMC6254351
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003302
Functional metagenomics identifies an exosialidase with an inverting catalytic mechanism that defines a new glycoside hydrolase family (GH156)
Abstract
Exosialidases are glycoside hydrolases that remove a single terminal sialic acid residue from oligosaccharides. They are widely distributed in biology, having been found in prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and certain viruses. Most characterized prokaryotic sialidases are from organisms that are pathogenic or commensal with mammals. However, in this study, we used functional metagenomic screening to seek microbial sialidases encoded by environmental DNA isolated from an extreme ecological niche, a thermal spring. Using recombinant expression of potential exosialidase candidates and a fluorogenic sialidase substrate, we discovered an exosialidase having no homology to known sialidases. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that this protein is a member of a small family of bacterial proteins of previously unknown function. Proton NMR revealed that this enzyme functions via an inverting catalytic mechanism, a biochemical property that is distinct from those of known exosialidases. This unique inverting exosialidase defines a new CAZy glycoside hydrolase family we have designated GH156.
Keywords: extremophile; functional metagenomics; glycoside hydrolase; glycosylation; high-throughput screening (HTS); inverting mechanism; neuraminidase; sialic acid; sialidase.
© 2018 Chuzel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
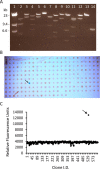


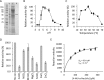


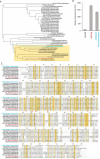
Similar articles
-
Human Gut Metagenomes Encode Diverse GH156 Sialidases.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Dec 13;88(23):e0175522. doi: 10.1128/aem.01755-22. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36394327 Free PMC article.
-
A New Group of Modular Xylanases in Glycoside Hydrolase Family 8 from Marine Bacteria.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Nov 15;84(23):e01785-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01785-18. Print 2018 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30217847 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a halotolerant, cold-active marine endo-β-1,4-glucanase by using functional metagenomics of seaweed-associated microbiota.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Aug;80(16):4958-67. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01194-14. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24907332 Free PMC article.
-
Features and applications of bacterial sialidases.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Jul;91(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3307-2. Epub 2011 May 5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21544654 Review.
-
Diversity of sialidases found in the human body - A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Apr 1;148:857-868. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.123. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 31945439 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of a New Temperate Escherichia coli Phage vB_EcoP_ZX5 and Its Regulatory Protein.Pathogens. 2022 Nov 30;11(12):1445. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11121445. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36558779 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Use of Microbial Community Genomes in Various Dimensions of Agriculture Productivity and Its Management: A Review.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 17;13:708335. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.708335. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35655999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of a functional system for recombinant production of secreted proteins at 50 °C in the thermophilic Bacillus methanolicus.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Jul 28;19(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01409-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 32723337 Free PMC article.
-
Carbohydrate-active enzyme (CAZyme) discovery and engineering via (Ultra)high-throughput screening.RSC Chem Biol. 2024 May 23;5(7):595-616. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00024b. eCollection 2024 Jul 3. RSC Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38966674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pangenome analysis provides insights into the genetic diversity, metabolic versatility, and evolution of the genus Flavobacterium.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 18;11(5):e0100323. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01003-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37594286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maruthamuthu M., Jiménez D. J., Stevens P., and van Elsas J. D. (2016) A multi-substrate approach for functional metagenomics-based screening for (hemi)cellulases in two wheat straw-degrading microbial consortia unveilsnovel thermoalkaliphilic enzymes. BMC Genomics. 17, 86 10.1186/s12864-016-2404-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

