Critical role for the Ly49 family of class I MHC receptors in adaptive natural killer cell responses
- PMID: 30249666
- PMCID: PMC6233086
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1722374115
Critical role for the Ly49 family of class I MHC receptors in adaptive natural killer cell responses
Abstract
Adaptive natural killer (NK) cell memory represents a new frontier in immunology. Work over the last decade has discovered and confirmed the existence of NK cells with antigen-specific memories, which had previously been considered a unique property of T and B cells. These findings have shown that antigen-specific NK cells gain their specificity without the use of RAG proteins, representing a novel mechanism for generating antigen specificity, but the details of this mechanism have remained a mystery. We have discovered that members of the Ly49 family of surface receptors are critically involved in both the sensitization and the challenge phases of an NK cell memory response, as is antigen presentation from their binding partner, the class I MHC. Moreover, we demonstrate that the Ly49-interacting component of a presented antigen dictates the specificity of the NK cell memory response, implicating Ly49 receptors themselves in antigen-specific recognition. Finally, we demonstrate that adaptive NK cell memories can protect against an otherwise lethal melanoma without T cell or B cell support. These findings offer insight into the mechanism behind NK cell antigen specificity and demonstrate the clinical potential of this adaptive immune cell.
Keywords: Ly49 receptors; adaptive memory; cancer vaccines; immune memory; natural killer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
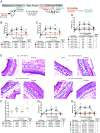
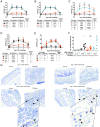

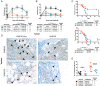
Comment in
-
Natural killer cells might adapt their inhibitory receptors for memory.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):11357-11359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815756115. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30337482 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- O’Leary JG, Goodarzi M, Drayton DL, von Andrian UH. T cell- and B cell-independent adaptive immunity mediated by natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:507–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

