Novel mutation in the CHST14 gene causing musculocontractural type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- PMID: 30249733
- PMCID: PMC6157554
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-226165
Novel mutation in the CHST14 gene causing musculocontractural type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Abstract
Musculocontractural type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (MC-EDS) is a recently recognised connective tissue disorder. MC-EDS is caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutation in the carbohydrate sulfotransferase 14 (CHST14) gene on chromosome 15q15. Herein, we report a case of a 3-year-old boy with MC-EDS in whom a novel mutation in the CHST14 gene was discovered. Besides being the second report of this rare disorder from India, the child till 3 years has not had any bleeding tendency as described in the earlier reports of this disorder.
Keywords: developmental paediatrocs; genetics; musculoskeletal and joint disorders.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2018. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


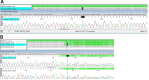
References
-
- Steinmann B, Royce PM, Superti-Furga A. The Ehlers-Danlos syndrome : Royce PM, Steinmann B, Connective tissue and its heritable disorders. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2002:431–523.
-
- Beighton P, De Paepe A, Steinmann B, et al. Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: revised nosology, Villefranche, 1997. Ehlers-Danlos National Foundation (USA) and Ehlers-Danlos Support Group (UK). Am J Med Genet 1998;77:31–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
