Bioprocessing of Functional Ingredients from Flaxseed
- PMID: 30250012
- PMCID: PMC6222892
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23102444
Bioprocessing of Functional Ingredients from Flaxseed
Abstract
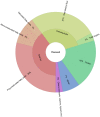
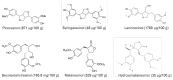
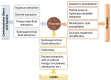
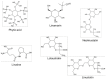
Flaxseeds (Linum usitatissimum L.) are oilseeds endowed with nutritional constituents such as lignans, lipids, proteins, fibre, carbohydrates, and micronutrients. Owing to their established high nutritional profile, flaxseeds have gained an established reputation as a dietary source of high value functional ingredients. Through the application of varied bioprocessing techniques, these essential constituents in flaxseeds can be made bioavailable for different applications such as nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and food industry. However, despite their food and health applications, flaxseeds contain high levels of phytotoxic compounds such as linatine, phytic acids, protease inhibitors, and cyanogenic glycosides. Epidemiological studies have shown that the consumption of these compounds can lead to poor bioavailability of essential nutrients and/or health complications. As such, these components must be removed or inactivated to physiologically undetectable limits to render flaxseeds safe for consumption. Herein, critical description of the types, characteristics, and bioprocessing of functional ingredients in flaxseed is presented.
Keywords: bio-refinery; bioactive compounds; bioprocessing; detoxification; flaxseed; functional food; nutraceuticals.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Nutritional value and functional properties of flaxseed].Vopr Pitan. 2012;81(3):4-10. Vopr Pitan. 2012. PMID: 22888664 Review. Russian.
-
A comprehensive review of flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.): health-affecting compounds, mechanism of toxicity, detoxification, anticancer and potential risk.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(32):11081-11104. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2092718. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 35833457 Review.
-
Insight into the Influence of Cultivar Type, Cultivation Year, and Site on the Lignans and Related Phenolic Profiles, and the Health-Promoting Antioxidant Potential of Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) Seeds.Molecules. 2018 Oct 14;23(10):2636. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102636. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30322184 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Linum usitatissimum Medicinal Plant: Its Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Ethnomedicinal Uses.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(18):2801-2834. doi: 10.2174/1389557521666210203153436. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33535948 Review.
-
Comparison of phytochemical profiles and health benefits in fiber and oil flaxseeds (Linum usitatissimum L.).Food Chem. 2017 Jan 1;214:227-233. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.075. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 27507470
Cited by
-
The Improved Quality of Gluten-Free Bread Due to the Use of Flaxseed Oil Cake: A Comprehensive Study Evaluating Nutritional Value, Technological Properties, and Sensory Quality.Foods. 2023 Nov 29;12(23):4320. doi: 10.3390/foods12234320. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38231753 Free PMC article.
-
Biotransformation of Flaxseed Oil Cake into Bioactive Camembert-Analogue Using Lactic Acid Bacteria, Penicillium camemberti and Geotrichum candidum.Microorganisms. 2020 Aug 20;8(9):1266. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8091266. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32825460 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of flaxseed flour as a partial replacement for wheat flour on the characteristics of Chinese steamed bread.RSC Adv. 2020 Jul 28;10(47):28114-28120. doi: 10.1039/d0ra05742h. eCollection 2020 Jul 27. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35519148 Free PMC article.
-
Development, Characterization, and Bioactivity of Non-Dairy Kefir-Like Fermented Beverage Based on Flaxseed Oil Cake.Foods. 2019 Nov 3;8(11):544. doi: 10.3390/foods8110544. Foods. 2019. PMID: 31684151 Free PMC article.
-
Flaxseed Ethanol Extracts' Antitumor, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Potential.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;11(5):892. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050892. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- US-FDA High linolenic acid flaxseed oil-grn no. 256. [(accessed on 27 August 2018)]; Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/?set=GRASNotices&id=256.
-
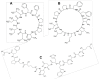
- Morita H., Shishido A., Matsumoto T., Itokawa H., Takeya K. Cyclolinopeptides b-e, new cyclic peptides from linum usitatissimum. Tetrahedron. 1999;55:967–976. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(98)01086-2. - DOI
-
- Rabetafika H.N., Van Remoortel V., Danthine S., Paquot M., Blecker C. Flaxseed proteins: Food uses and health benefits. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011;46:221–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2010.02477.x. - DOI
-
- Bekhit A.E.-D.A., Shavandi A., Jodjaja T., Birch J., Teh S., Mohamed A.I.A., Al-Juhaimi F.Y., Saeedi P., Bekhit A.A. Flaxseed: Composition, detoxification, utilization, and opportunities. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018;13:129–152. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2017.11.017. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

