Targeting proteasome-associated deubiquitinases as a novel strategy for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer
- PMID: 30250021
- PMCID: PMC6155249
- DOI: 10.1038/s41389-018-0086-y
Targeting proteasome-associated deubiquitinases as a novel strategy for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer
Abstract
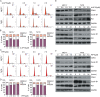
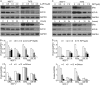
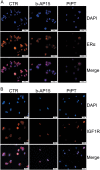
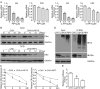
Estrogen receptor α (ERα) is expressed in ~67% of breast cancers and is critical to their proliferation and progression. The expression of ERα is regarded as a major prognostic marker, making it a meaningful target to treat breast cancer (BCa). However, hormone receptor-positive BCa was sometimes irresponsive or even resistant to classic anti-hormonal therapies (e.g., fulvestrant and tamoxifen). Hence, novel anti-endocrine therapies are urgent for ERα+ BCa. A phase II study suggested that bortezomib, an inhibitor blocking the activity of 20 S proteasomes, intervenes in cancer progression for anti-endocrine therapy in BCa. Here we report that proteasome-associated deubiquitinases (USP14 and UCHL5) inhibitors b-AP15 and platinum pyrithione (PtPT) induce growth inhibition in ERα+ BCa cells. Further studies show that these inhibitors induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis associated with caspase activation, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and the downregulation of ERα. Moreover, we suggest that b-AP15 and PtPT block ERα signaling via enhancing the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of ERα and inhibiting the transcription of ERα. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that proteasome-associated deubiquitinases inhibitors b-AP15 and PtPT may have the potential to treat BCa resistant to anti-hormonal therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Platinum-containing compound platinum pyrithione is stronger and safer than cisplatin in cancer therapy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:22-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.06.019. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27381943 Free PMC article.
-
ERα is a target for butein-induced growth suppression in breast cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 1;10(11):3721-3736. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33294263 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting proteasomal deubiquitinases USP14 and UCHL5 with b-AP15 reduces 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Dec;44(12):2537-2548. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01136-0. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37528233 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-Aided Ligand Discovery for Estrogen Receptor Alpha.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 12;21(12):4193. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124193. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32545494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteasome deubiquitinases as novel targets for cancer therapy.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Nov;44(11):1729-38. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.07.011. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22819849 Review.
Cited by
-
Glycine-Poly-L-Lactic Acid Copolymeric Nanoparticles for the Efficient Delivery of Bortezomib.Pharm Res. 2019 Sep 13;36(11):160. doi: 10.1007/s11095-019-2686-4. Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 31520196
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 regulates HIF-1α degradation to inhibit apoptosis in hypoxic cardiomyocytes.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Sep 16;7(1):242. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00629-3. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34531382 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ERα degradation by L-Tetrahydropalmatine provides a novel strategy for breast cancer treatment.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 May 18;16(12):2192-2204. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.44005. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549765 Free PMC article.
-
A SIX1 degradation inducer blocks excessive proliferation of prostate cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Mar 14;18(6):2439-2451. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.67873. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35414775 Free PMC article.
-
USP22 positively modulates ERα action via its deubiquitinase activity in breast cancer.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Nov;27(11):3131-3145. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0568-2. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 32494025 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

