Long noncoding RNA ROR promotes breast cancer by regulating the TGF-β pathway
- PMID: 30250400
- PMCID: PMC6145201
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-018-0638-4
Long noncoding RNA ROR promotes breast cancer by regulating the TGF-β pathway
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the leading cause of oncological mortality among women. Efficient detection of cancer cells in an early stage and potent therapeutic agents targeting metastatic tumors are highly needed to improve survival rates. Emerging evidence indicates that lncRNAs (long noncoding RNAs) are critical regulators of fundamental cellular processes in a variety of tumors including breast cancer. The functional details of these regulatory elements, however, remain largely unexplored.
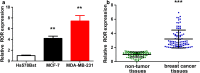
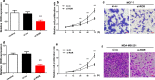
Methods: In this study, lncRNA ROR (linc-ROR) was examined by real-time PCR in different breast cancer cell lines and breast tumor tissues/non-tumor tissues were collected from both breast cancer patients and healthy controls. Linc-ROR was knockdown in breast cancer cell lines and the effects on cell proliferation, migration and invasion were tested both in vitro and in vivo tumor model. Effects of linc-ROR knockdown on TGF-β signaling pathway were investigated by Western blot.
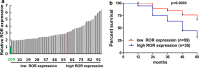
Results: Our studies have suggested that linc-ROR, a critical factor for embryonic stem cell maintenance, probably acts as an oncogenic factor in breast cancer cells, causing poor prognostic outcomes. Overexpression of linc-ROR seems to be responsible for promoting proliferation and invasion of cancer cells as well as tumor growth in nude mice. The regulatory action of linc-ROR can affect the activity of the TGF-β signaling pathway, which has been proven critical for mammary development and breast cancer.
Conclusions: The results have highlighted the potential importance of linc-ROR in the progression of advanced breast cancer, and thus will stimulate efforts in the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Long noncoding RNA; ROR; TGF-β.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Linc-ROR promotes the progression of breast cancer and decreases the sensitivity to rapamycin through miR-194-3p targeting MECP2.Mol Oncol. 2020 Sep;14(9):2231-2250. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12700. Epub 2020 May 24. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32335998 Free PMC article.
-
Linc-RoR promotes MAPK/ERK signaling and confers estrogen-independent growth of breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2017 Oct 17;16(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0727-3. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29041978 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of Long Noncoding RNA Regulator of Reprogramming in Cancer Treatment.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jul 21;12:6103-6112. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S253042. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32765105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linc-ROR Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Functioning as a Competing Endogenous RNA for miR-138 and miR-145.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018 Jun 1;11:345-353. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018. PMID: 29858070 Free PMC article.
-
Relevance Function of Linc-ROR in the Pathogenesis of Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 11;8:696. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00696. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850817 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FOXM1 Promotes Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Activation of the Linc-ROR/LMO4/AKT/PI3K Axis.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 10;11:658712. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.658712. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34447693 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic predisposition and prediction protocol for epithelial neoplasms in disease-free individuals: A systematic review.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2020 May-Aug;24(2):293-307. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_348_19. Epub 2020 Sep 9. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2020. PMID: 33456239 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators for Targeting Breast Cancer Stem Cells and Tumor Immune Microenvironment: Biological Properties and Therapeutic Potential.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;16(2):290. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020290. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the TP53INP1/TP53I3 axis for inhibition of colorectal cancer cell proliferation through MEG3 and Linc-ROR Co-expression.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 10;10(14):e34075. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34075. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39108882 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNAs as the critical regulators of PI3K/AKT, TGF-β, and MAPK signaling pathways during breast tumor progression.J Transl Med. 2023 Aug 18;21(1):556. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04434-7. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37596669 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steiner E, Klubert D, Knutson D. Assessing breast cancer risk in women. Am Fam Physician. 2008;78(12):1361–1366. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

