Posterior Tibial Neuropathy Secondary to Pseudoaneurysm of the Proximal Segment of the Anterior Tibial Artery with Delayed Onset
- PMID: 30250498
- PMCID: PMC6141260
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1669403
Posterior Tibial Neuropathy Secondary to Pseudoaneurysm of the Proximal Segment of the Anterior Tibial Artery with Delayed Onset
Abstract
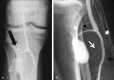
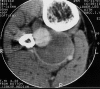
Anterior tibial artery is a nonvital artery which is one of the three arteries of the leg. This artery has a short proximal l segment in the popliteal region and a long segment in the anterior compartment of the leg designated as distal segment. With consideration of the deep location of the proximal segment in the popliteal fossa, it is less susceptible to trauma and subsequent formation of an aneurysm. On the contrary, the superficial long distal segment is more susceptible to trauma with high chance of pseudoaneurysm formation at the site of unrecognized injury. In this article, a 38-year-old military man being manifested about a decade after a trivial missile fragment injury with progressive posterior tibial neuropathy is presented. A giant pseudoaneurysm arising from the proximal segment of the anterior tibial artery was confirmed with angiography and the exact size of this pathology was documented with contrasted computed tomographic scan. The aneurysmal sac removal was accomplished after ligation of the corresponding artery proximal and distal to the sac followed by tibial nerve neurolysis which result in full recovery. In careful review we found that neither pseudoaneurysm arising from the proximal tibial artery nor posterior tibial neuropathy due to the compressive effect of the aneurysmal sac of this segment has been reported previously. Our primary purpose for reporting this case is not to describe the rarity of pseudoaneurysm formation at proximal segment of this artery but rather to describe delayed-onset posterior tibial vascular compressive neuropathy due to such an aneurysm. Eventually due to the potential sequel of a pseudoaneurysm, it is important for the surgeons to have high index of suspicion to prevent a missed or delayed diagnosis.
Keywords: anterior tibial artery; missile fragment; posterior tibial neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peroneal/posterior tibial nerves delayed dysfunction due to traumatic popliteal artery pseudoaneurysm resulting from trivial stab wound: A case report.Surg Neurol Int. 2021 Sep 30;12:488. doi: 10.25259/SNI_770_2021. eCollection 2021. Surg Neurol Int. 2021. PMID: 34754538 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous Anterior Tibial Artery Avulsion and Tibio-Peroneal Trunk Transection Resulting into a Pseudoaneurysm: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2017 Jan 26;18:90-95. doi: 10.12659/ajcr.901925. Am J Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28123173 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery after interlocking tibial nailing: an unexpected complication.Eur J Med Res. 2016 Sep 29;21(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40001-016-0231-z. Eur J Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27687142 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular Treatment of an Anterior Tibial Artery Pseudoaneurysm Secondary to Penetrating Trauma in a Young Patient: Case Report and Literature Review.Ann Vasc Surg. 2019 Oct;60:479.e5-479.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Ann Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 31195105 Review.
-
[Post-traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery secondary to tibial shaft fracture. Case report].Acta Ortop Mex. 2016 Jan-Feb;30(1):25-7. Acta Ortop Mex. 2016. PMID: 27627775 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Peroneal/posterior tibial nerves delayed dysfunction due to traumatic popliteal artery pseudoaneurysm resulting from trivial stab wound: A case report.Surg Neurol Int. 2021 Sep 30;12:488. doi: 10.25259/SNI_770_2021. eCollection 2021. Surg Neurol Int. 2021. PMID: 34754538 Free PMC article.
-
Pathology of Critical Limb Ischemia; Comparison of Plaque Characteristics Between Anterior and Posterior Tibial Arteries.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2023 Dec 1;30(12):1893-1904. doi: 10.5551/jat.64259. Epub 2023 Jun 17. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2023. PMID: 37331812 Free PMC article.
-
Compressive median neuropathy caused by brachial artery pseudoaneurysm.Surg Neurol Int. 2024 Jan 12;15:11. doi: 10.25259/SNI_665_2023. eCollection 2024. Surg Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 38344104 Free PMC article.
-
Open Repair of a Giant Popliteal Artery Aneurysm Presenting with Nerve Compression Symptoms.Vasc Specialist Int. 2021 Mar 31;37(1):37-40. doi: 10.5758/vsi.200077. Vasc Specialist Int. 2021. PMID: 33795552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rich N M, Hobson R W, II, Collins G J., Jr Traumatic arteriovenous fistulas and false aneurysms: a review of 558 lesions. Surgery. 1975;78(06):817–828. - PubMed
-
- Sturm J T, Bodily K C, Rothenberger D A, Perry J F., Jr Arterial injuries of the extremities following blunt trauma. J Trauma. 1980;20(11):933–936. - PubMed
-
- Winn D F, Jr, Downs C R, Freeman N E. Traumatic aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas in war wounds. U S Armed Forces Med J. 1954;5(06):781–794. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

