Potential use of compounds from sea cucumbers as MDM2 and CXCR4 inhibitors to control cancer cell growth
- PMID: 30250516
- PMCID: PMC6144067
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6588
Potential use of compounds from sea cucumbers as MDM2 and CXCR4 inhibitors to control cancer cell growth
Abstract
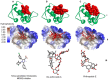
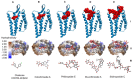
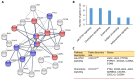
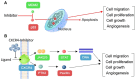
Ineffectiveness of cancer therapy may originate in the incompatibility of the treatment with various mutations in the cancer cells. Finding novel anticancer treatments that work efficiently for varying types of cancer cells remains challenging. Previous studies have identified that compounds in sea cucumbers are capable of inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and inducing apoptosis. However, information on the underlying mechanisms controlling cancer cell growth at a molecular level remains limited. The current study analyzed the potential of colochiroside A, ds-echinoside A, philinopside E, sphingosine and stichoposide C as inhibitors for anticancer target proteins, including mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) and C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4). Inhibition of MDM2 triggers apoptosis through regulation of tumor protein 53 and CXCR4 inhibition may prevent cancer cell proliferation and growth by affecting the Janus kinase 2/3 signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway and protein tyrosine kinase 2. The results of a binding affinity analysis using molecular docking revealed that philinopside E and ds-echinoside A may inhibit MDM2 and CXCR4. The data suggested that these active compounds may be promising inhibitors of cell growth by binding to two targets simultaneously. Furthermore, stichoposide C and colochiroside A were predicted to inhibit CXCR4. Additional research is needed to validate the in vitro activity of the aforementioned compounds.
Keywords: BioGRID; C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; Janus kinase 2/3; anticancer; apoptosis; mouse double minute 2 homolog; pathway analysis; sea cucumber.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sea Cucumber Compounds Targeting NF-κB in Cancer Treatment.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2022 Apr 17;16:11779322221091740. doi: 10.1177/11779322221091740. eCollection 2022. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2022. PMID: 35462875 Free PMC article.
-
Echinoside A, a new marine-derived anticancer saponin, targets topoisomerase2alpha by unique interference with its DNA binding and catalytic cycle.Ann Oncol. 2010 Mar;21(3):597-607. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp335. Epub 2009 Sep 22. Ann Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19773249
-
Sea cucumber extract TBL-12 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human prostate cancer cells through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and intrinsic caspase apoptosis pathway.Prostate. 2019 Jun;79(8):826-839. doi: 10.1002/pros.23788. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Prostate. 2019. PMID: 30889629
-
Pleiotropic effects of methionine adenosyltransferases deregulation as determinants of liver cancer progression and prognosis.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):830-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.031. Epub 2013 May 7. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23665184 Review.
-
Targeted abrogation of diverse signal transduction cascades by emodin for the treatment of inflammatory disorders and cancer.Cancer Lett. 2013 Dec 1;341(2):139-49. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.023. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23962559 Review.
Cited by
-
Stichoposide C Exerts Anticancer Effects on Ovarian Cancer by Inducing Autophagy via Inhibiting AKT/mTOR Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2022 Jan 21;15:87-101. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S340556. eCollection 2022. Onco Targets Ther. 2022. PMID: 35087279 Free PMC article.
-
Sea Cucumber (Stichopus japonicas) F2 Enhanced TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis via XIAP Ubiquitination and ER Stress in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Nutrients. 2019 May 11;11(5):1061. doi: 10.3390/nu11051061. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31083595 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of phenylalanine dehydrogenase from Thermoactinomyces intermedius for the production of a novel homoglutamate.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 30;17(3):e0263784. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263784. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35353822 Free PMC article.
-
Sea Cucumber Compounds Targeting NF-κB in Cancer Treatment.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2022 Apr 17;16:11779322221091740. doi: 10.1177/11779322221091740. eCollection 2022. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2022. PMID: 35462875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wargasetia TL, Permana S, Widodo The role of sea cucumber active compound and its derivative as an anti-cancer agent. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2018;4:27–32. doi: 10.1007/s40495-018-0121-x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
