Leptin induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via activation of the ERK signaling pathway in lung cancer cells
- PMID: 30250542
- PMCID: PMC6144616
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9230
Leptin induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via activation of the ERK signaling pathway in lung cancer cells
Abstract
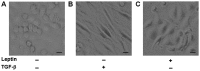
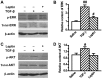
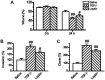
Previous studies revealed that leptin induces the growth and proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis of lung cancer cells. However, the effect of leptin on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is not yet clear. In the present study, the effect of leptin on EMT was investigated as well as its underlying mechanisms in A549 cells. The ability of leptin to induce EMT was investigated by microscopic examination and western blotting. The impacts of leptin on cell migration, invasion and tumorigenesis were evaluated by wound healing, Transwell and colony formation assays, respectively. It was demonstrated that leptin induced EMT-associated morphological changes, namely a decrease in cell-cell contact and a more elongated morphological shape. Leptin decreased the expression levels of epithelial phenotype markers E-cadherin and keratin, increased the expression of mesenchymal phenotype marker Vimentin, and raised the expression of EMT-induced transcription factor ZEB-1. In addition, leptin activated the extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway and did not affect the activation of the protein kinase B signaling pathway in A549 cells. Leptin also promoted EMT-induced migration, invasion and tumorigenesis in vitro in A549 cells. The present study provides evidence that leptin induced EMT via the activation of the ERK signaling pathway and increased EMT-induced tumor phenotypes in lung cancer cells. These findings suggest that leptin may be a promising target for lung cancer treatment through the regulation of EMT.
Keywords: epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; extracellular signal regulated kinase; invasion; leptin; metastasis; tumorigensis.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
