Structured lifestyle education for people with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and first-episode psychosis (STEPWISE): randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 30251622
- PMCID: PMC6330076
- DOI: 10.1192/bjp.2018.167
Structured lifestyle education for people with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and first-episode psychosis (STEPWISE): randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a major challenge for people with schizophrenia.AimsWe assessed whether STEPWISE, a theory-based, group structured lifestyle education programme could support weight reduction in people with schizophrenia.
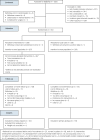
Method: In this randomised controlled trial (study registration: ISRCTN19447796), we recruited adults with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder or first-episode psychosis from ten mental health organisations in England. Participants were randomly allocated to the STEPWISE intervention or treatment as usual. The 12-month intervention comprised four 2.5 h weekly group sessions, followed by 2-weekly maintenance contact and group sessions at 4, 7 and 10 months. The primary outcome was weight change after 12 months. Key secondary outcomes included diet, physical activity, biomedical measures and patient-related outcome measures. Cost-effectiveness was assessed and a mixed-methods process evaluation was included.
Results: Between 10 March 2015 and 31 March 2016, we recruited 414 people (intervention 208, usual care 206) with 341 (84.4%) participants completing the trial. At 12 months, weight reduction did not differ between groups (mean difference 0.0 kg, 95% CI -1.6 to 1.7, P = 0.963); physical activity, dietary intake and biochemical measures were unchanged. STEPWISE was well-received by participants and facilitators. The healthcare perspective incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was £246 921 per quality-adjusted life-year gained.
Conclusions: Participants were successfully recruited and retained, indicating a strong interest in weight interventions; however, the STEPWISE intervention was neither clinically nor cost-effective. Further research is needed to determine how to manage overweight and obesity in people with schizophrenia.Declaration of interestR.I.G.H. received fees for lecturing, consultancy work and attendance at conferences from the following: Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Lundbeck, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Otsuka, Sanofi, Sunovion, Takeda, MSD. M.J.D. reports personal fees from Novo Nordisk, Sanofi-Aventis, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Servier, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Takeda Pharmaceuticals International Inc.; and, grants from Novo Nordisk, Sanofi-Aventis, Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen. K.K. has received fees for consultancy and speaker for Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi-Aventis, Lilly, Servier and Merck Sharp & Dohme. He has received grants in support of investigator and investigator-initiated trials from Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi-Aventis, Lilly, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim and Merck Sharp & Dohme. K.K. has received funds for research, honoraria for speaking at meetings and has served on advisory boards for Lilly, Sanofi-Aventis, Merck Sharp & Dohme and Novo Nordisk. D.Sh. is expert advisor to the NICE Centre for guidelines; board member of the National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health (NCCMH); clinical advisor (paid consultancy basis) to National Clinical Audit of Psychosis (NCAP); views are personal and not those of NICE, NCCMH or NCAP. J.P. received personal fees for involvement in the study from a National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) grant. M.E.C. and Y.D. report grants from NIHR Health Technology Assessment, during the conduct of the study; and The Leicester Diabetes Centre, an organisation (employer) jointly hosted by an NHS Hospital Trust and the University of Leicester and who is holder (through the University of Leicester) of the copyright of the STEPWISE programme and of the DESMOND suite of programmes, training and intervention fidelity framework that were used in this study. S.R. has received honorarium from Lundbeck for lecturing. F.G. reports personal fees from Otsuka and Lundbeck, personal fees and non-financial support from Sunovion, outside the submitted work; and has a family member with professional links to Lilly and GSK, including shares. F.G. is in part funded by the National Institute for Health Research Collaboration for Leadership in Applied Health Research & Care Funding scheme, by the Maudsley Charity and by the Stanley Medical Research Institute and is supported by the by the Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King's College London.
Keywords: Schizophrenia; antipsychotic; cost benefit analysis; exercise; healthy diet; lifestyle; obesity; overweight; psychosis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Promoting weight loss in people with schizophrenia: what do we still need to learn before implementing lifestyle interventions?Br J Psychiatry. 2019 Feb;214(2):74-75. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2018.252. Br J Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30681054
Similar articles
-
Treatment-resistant and multi-therapy-resistant criteria for bipolar depression: consensus definition.Br J Psychiatry. 2019 Jan;214(1):27-35. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2018.257. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Br J Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30520709 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine: stimulating antidepressant treatment?BJPsych Open. 2016 May 11;2(3):e5-e9. doi: 10.1192/bjpo.bp.116.002923. eCollection 2016 May. BJPsych Open. 2016. PMID: 27703782 Free PMC article.
-
Structured lifestyle education to support weight loss for people with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and first episode psychosis: the STEPWISE RCT.Health Technol Assess. 2018 Nov;22(65):1-160. doi: 10.3310/hta22650. Health Technol Assess. 2018. PMID: 30499443 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cardiovascular Outcomes with Once-Weekly GLP-1 RAs: Clinical and Economic Implications.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018 Sep;24(9-a Suppl):S42-S52. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2018.24.9-a.s42. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30156446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health-Related Quality of Life Assessments with Once-Weekly Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018 Sep;24(9-a Suppl):S30-S41. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2018.24.9-a.s30. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30156447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influencing factors of obesity in community patients with deficit schizophrenia: a cross-sectional study.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Jun 11;27(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00706-y. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35690794 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotic-Induced Weight Gain in Severe Mental Illness: Risk Factors and Special Considerations.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2023 Nov;25(11):707-721. doi: 10.1007/s11920-023-01458-0. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2023. PMID: 37755655 Review.
-
Home-based Intervention with Semaglutide Treatment of Neuroleptic-Related Prediabetes (HISTORI): protocol describing a prospective, randomised, placebo controlled and double-blinded multicentre trial.BMJ Open. 2024 Mar 18;14(3):e077173. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-077173. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38503415 Free PMC article.
-
Psychosocial Interventions Impact on Cardiometabolic, Neurobiological, Behavioral, and Immune Outcomes in People With a Serious Mental Illness: A Systematic Review.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 21;8(7):e70954. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70954. eCollection 2025 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40692574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between Antipsychotic Medication Use and Diabetes.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Sep 2;19(10):96. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1220-8. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31478094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holt RI, Peveler RC. Obesity, serious mental illness and antipsychotic drugs. Diabetes Obes Metab 2009; 11: 665–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

