Multiple Puf proteins regulate the stability of ribosome biogenesis transcripts
- PMID: 30251908
- PMCID: PMC6284577
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1521211
Multiple Puf proteins regulate the stability of ribosome biogenesis transcripts
Abstract
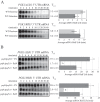
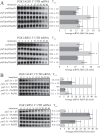
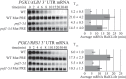
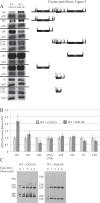
Cells must make careful use of the resources available to them. A key area of cellular regulation involves the biogenesis of ribosomes. Transcriptional regulation of ribosome biogenesis factor genes through alterations in histone acetylation has been well studied. This work identifies a post-transcriptional mechanism of ribosome biogenesis regulation by Puf protein control of mRNA stability. Puf proteins are eukaryotic mRNA binding proteins that play regulatory roles in mRNA degradation and translation via association with specific conserved elements in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNAs and with degradation and translation factors. We demonstrate that several ribosome biogenesis factor mRNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing a canonical Puf4p element in their 3' UTRs are destabilized by Puf2p, Puf4, and Puf5p, yet stabilized by Puf1p and Puf3p. In the absence of all Puf proteins, these ribosome biogenesis mRNAs are destabilized by a secondary mechanism involving the same 3' UTR element. Unlike other targets of Puf4p regulation, the decay of these transcripts is not altered by carbon source. Overexpression of Puf4p results in delayed ribosomal RNA processing and altered ribosomal subunit trafficking. These results represent a novel role for Puf proteins in yeast as regulators of ribosome biogenesis transcript stability.
Keywords: 3ʹ UTR; Mrna decay; Puf proteins; Pumilio; mRNA stability; ribosome biogenesis; yeast.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Conditional regulation of Puf1p, Puf4p, and Puf5p activity alters YHB1 mRNA stability for a rapid response to toxic nitric oxide stress in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Mar 15;26(6):1015-29. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-10-1452. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25631823 Free PMC article.
-
Puf1p acts in combination with other yeast Puf proteins to control mRNA stability.RNA. 2008 Feb;14(2):246-62. doi: 10.1261/rna.847408. Epub 2007 Dec 19. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18094119 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive association of functionally and cytotopically related mRNAs with Puf family RNA-binding proteins in yeast.PLoS Biol. 2004 Mar;2(3):E79. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020079. Epub 2004 Mar 16. PLoS Biol. 2004. PMID: 15024427 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Puf proteins in mRNA degradation and translation.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Jul-Aug;2(4):471-92. doi: 10.1002/wrna.69. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957038 Review.
-
The PUF Protein Family: Overview on PUF RNA Targets, Biological Functions, and Post Transcriptional Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 30;19(2):410. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020410. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29385744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Puf4 Mediates Post-transcriptional Regulation of Cell Wall Biosynthesis and Caspofungin Resistance in Cryptococcus neoformans.mBio. 2021 Jan 12;12(1):e03225-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03225-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33436441 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct RNA-binding modules in a single PUF protein cooperate to determine RNA specificity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Sep 19;47(16):8770-8784. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz583. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31294800 Free PMC article.
-
Rpb4 and Puf3 imprint and post-transcriptionally control the stability of a common set of mRNAs in yeast.RNA Biol. 2021 Aug;18(8):1206-1220. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1839229. Epub 2020 Nov 1. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33094674 Free PMC article.
-
Species-aware DNA language models capture regulatory elements and their evolution.Genome Biol. 2024 Apr 2;25(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03221-x. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 38566111 Free PMC article.
-
Puf6 and Loc1 Are the Dedicated Chaperones of Ribosomal Protein Rpl43 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 26;20(23):5941. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235941. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31779129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osheim YN, French SL, Keck KM, et al. Pre-18S ribosomal RNA is structurally compacted into the SSU processome prior to being cleaved from nascent transcripts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell. 2004. December 22;16(6):943–954. PubMed PMID: 15610737. - PubMed
-
- Warner JR. The economics of ribosome biosynthesis in yeast. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999. November;24(11):437–440. PubMed PMID: 10542411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
