Structure of the human epithelial sodium channel by cryo-electron microscopy
- PMID: 30251954
- PMCID: PMC6197857
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.39340
Structure of the human epithelial sodium channel by cryo-electron microscopy
Abstract
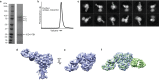
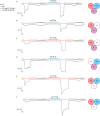
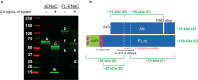
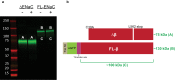
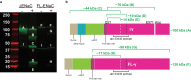
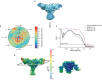
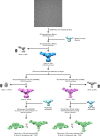
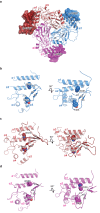
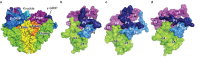
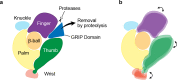
The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), a member of the ENaC/DEG superfamily, regulates Na+ and water homeostasis. ENaCs assemble as heterotrimeric channels that harbor protease-sensitive domains critical for gating the channel. Here, we present the structure of human ENaC in the uncleaved state determined by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. The ion channel is composed of a large extracellular domain and a narrow transmembrane domain. The structure reveals that ENaC assembles with a 1:1:1 stoichiometry of α:β:γ subunits arranged in a counter-clockwise manner. The shape of each subunit is reminiscent of a hand with key gating domains of a 'finger' and a 'thumb.' Wedged between these domains is the elusive protease-sensitive inhibitory domain poised to regulate conformational changes of the 'finger' and 'thumb'; thus, the structure provides the first view of the architecture of inhibition of ENaC.
Keywords: Cryo-EM; Ion Channel; electrophysiology; heterotrimer; human; molecular biophysics; structural biology; structure.
© 2018, Noreng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SN, AB, RP, CY, IB No competing interests declared
Figures







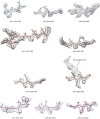
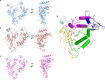
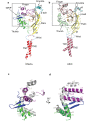

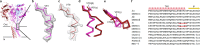
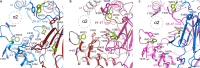
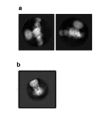
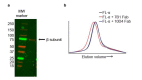
Similar articles
-
Molecular principles of assembly, activation, and inhibition in epithelial sodium channel.Elife. 2020 Jul 30;9:e59038. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59038. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32729833 Free PMC article.
-
ASIC and ENaC type sodium channels: conformational states and the structures of the ion selectivity filters.FEBS J. 2017 Feb;284(4):525-545. doi: 10.1111/febs.13840. Epub 2016 Sep 15. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 27580245 Review.
-
Thumb domains of the three epithelial Na+ channel subunits have distinct functions.J Biol Chem. 2018 Nov 9;293(45):17582-17592. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003618. Epub 2018 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30228189 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteine palmitoylation of the γ subunit has a dominant role in modulating activity of the epithelial sodium channel.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 16;289(20):14351-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526020. Epub 2014 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24692558 Free PMC article.
-
Insight toward epithelial Na+ channel mechanism revealed by the acid-sensing ion channel 1 structure.IUBMB Life. 2008 Sep;60(9):620-8. doi: 10.1002/iub.89. IUBMB Life. 2008. PMID: 18459164 Review.
Cited by
-
Taste transduction and channel synapses in taste buds.Pflugers Arch. 2021 Jan;473(1):3-13. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02464-4. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Pflugers Arch. 2021. PMID: 32936320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular principles of assembly, activation, and inhibition in epithelial sodium channel.Elife. 2020 Jul 30;9:e59038. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59038. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32729833 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acids regulate the epithelial Na+ channel in native tissues through direct binding at multiple sites.J Physiol. 2022 Nov;600(21):4695-4711. doi: 10.1113/JP283318. Epub 2022 Sep 23. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36071685 Free PMC article.
-
New insights regarding epithelial Na+ channel regulation and its role in the kidney, immune system and vasculature.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019 Mar;28(2):113-119. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000479. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 30585851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium Imbalance in Mice Results Primarily in Compensatory Gene Regulatory Responses in Kidney and Colon, but Not in Taste Tissue.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 3;12(4):995. doi: 10.3390/nu12040995. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32260115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Jain S, Kapral GJ, Grosse Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner RD, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. The Phenix software for automated determination of macromolecular structures. Methods. 2011;55:94–106. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2011.07.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruns JB, Carattino MD, Sheng S, Maarouf AB, Weisz OA, Pilewski JM, Hughey RP, Kleyman TR. Epithelial na+ channels are fully activated by furin- and prostasin-dependent release of an inhibitory peptide from the gamma-subunit. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2007;282:6153–6160. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610636200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

