Brain Penetrating Bifunctional Erythropoietin-Transferrin Receptor Antibody Fusion Protein for Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 30252487
- PMCID: PMC6457666
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00594
Brain Penetrating Bifunctional Erythropoietin-Transferrin Receptor Antibody Fusion Protein for Alzheimer's Disease
Erratum in
-
A Brain Penetrating Bifunctional Erythropoietin-Transferrin Receptor Antibody Fusion Protein for Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Pharm. 2020 Jan 6;17(1):360. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b01211. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31804843 No abstract available.
Abstract
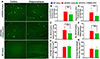
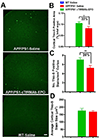
Erythropoietin (EPO), a glycoprotein cytokine essential to hematopoiesis, has neuroprotective effects in rodent models of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, high therapeutic doses or invasive routes of administration of EPO are required to achieve effective brain concentrations due to low blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetrability, and high EPO doses result in hematopoietic side effects. These obstacles can be overcome by engineering a BBB-penetrable analog of EPO, which is rapidly cleared from the blood, by fusing EPO to a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting the transferrin receptor (cTfRMAb), which acts as a molecular Trojan horse to ferry the EPO into the brain via the transvascular route. In the current study, we investigated the effects of the BBB-penetrable analog of EPO on AD pathology in a double transgenic mouse model of AD. Five and a half month old male APPswe/PSEN1dE9 (APP/PS1) transgenic mice were treated with saline ( n = 10) or the BBB-penetrable EPO ( n = 10) 3 days/week intraperitoneally for 8 weeks, compared to same-aged C57BL/6J wild-type mice treated with saline ( n = 8) with identical regiment. At 9 weeks following treatment initiation, exploration and spatial memory were assessed with the open-field and Y-maze test, mice were sacrificed, and brains were evaluated for Aβ peptide load, synaptic loss, BBB disruption, microglial activation, and microhemorrhages. APP/PS1 mice treated with the BBB-penetrable cTfRMAb-EPO fusion protein had significantly lower cortical and hippocampal Aβ peptide number ( p < 0.05) and immune-positive area ( p < 0.05), a decrease in hippocampal synaptic loss ( p < 0.05) and cortical microglial activation ( p < 0.001), and improved spatial memory ( p < 0.05) compared with APP/PS1 saline controls. BBB-penetrating EPO was not associated with microhemorrhage development. The cTfRMAb-EPO fusion protein offers therapeutic benefits by targeting multiple targets of AD pathogenesis and progression (Aβ load, synaptic loss, microglial activation) and improving spatial memory in the APP/PS1 mouse model of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; blood−brain barrier; erythropoietin; monoclonal antibody; transcytosis; transferrin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
William Pardridge is a consultant to and Ruben Boado is an employee of ArmaGen, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Blood-Brain Barrier Penetrating Biologic TNF-α Inhibitor for Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Pharm. 2017 Jul 3;14(7):2340-2349. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00200. Epub 2017 May 31. Mol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28514851
-
Plasma Pharmacokinetics of High-Affinity Transferrin Receptor Antibody-Erythropoietin Fusion Protein is a Function of Effector Attenuation in Mice.Mol Pharm. 2019 Aug 5;16(8):3534-3543. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00369. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31199881 Free PMC article.
-
Hematologic safety of chronic brain-penetrating erythropoietin dosing in APP/PS1 mice.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2019 Oct 17;5:627-636. doi: 10.1016/j.trci.2019.09.003. eCollection 2019. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2019. PMID: 31660425 Free PMC article.
-
The Promises and Challenges of Erythropoietin for Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Neuromolecular Med. 2019 Mar;21(1):12-24. doi: 10.1007/s12017-019-08524-y. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Neuromolecular Med. 2019. PMID: 30656553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood-brain barrier drug delivery of IgG fusion proteins with a transferrin receptor monoclonal antibody.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 Feb;12(2):207-22. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.952627. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25138991 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Cancer Chemotherapy through a Delivery System across the Blood-Brain Barrier into the Brain Based on Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis Using Monoclonal Antibody Conjugates.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 5;10(7):1597. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071597. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic LRP-1 plays an important role in amyloidosis in Alzheimer's disease mice: Potential role in chronic heavy alcohol feeding.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Sep;199:106570. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106570. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 38885850 Free PMC article.
-
TMEM16F may be a new therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Mar;18(3):643-651. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.350211. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36018189 Free PMC article.
-
Biologic TNF-α inhibitors reduce microgliosis, neuronal loss, and tau phosphorylation in a transgenic mouse model of tauopathy.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Dec 31;18(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02332-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34972522 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodegeneration, memory loss, and dementia: the impact of biological clocks and circadian rhythm.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021 Sep 30;26(9):614-627. doi: 10.52586/4971. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021. PMID: 34590471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun ZK; Yang HQ; Pan J; Zhen H; Wang ZQ; Chen SD; Ding JQ, Protective effects of erythropoietin on tau phosphorylation induced by beta-amyloid. J Neurosci Res 2008, 86 (13), 3018–27. - PubMed
-
- Brines M; Cerami A, Emerging biological roles for erythropoietin in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 2005, 6 (6), 484–94. - PubMed
-
- Li G; Ma R; Huang C; Tang Q; Fu Q; Liu H; Hu B; Xiang J, Protective effect of erythropoietin on beta-amyloid-induced PC12 cell death through antioxidant mechanisms. Neurosci Lett 2008, 442 (2), 143–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

