Comparison of rituximab and conventional adjuvant therapy for pemphigus vulgaris: A retrospective analysis
- PMID: 30252855
- PMCID: PMC6155499
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198074
Comparison of rituximab and conventional adjuvant therapy for pemphigus vulgaris: A retrospective analysis
Abstract
Background: Rituximab is a promising steroid sparing agent used in the treatment of moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris. Its exact place in the algorithm of pemphigus treatment, vis-à-vis other, conventional adjuvant therapy (CAT) is not known.
Objective: To describe and compare disease course outcomes and morbidity among patients with moderate to severe pemphigus who received rituximab therapy (RT) in addition to prednisone and CAT, versus those who were treated with prednisone and CAT alone.
Methods: A 16-year retrospective case control study was designed with adult patients who were seen at the Duke University Dermatology Immunodermatology clinic from 1999-2015, who had a diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris, and required prednisone and at least 1 systemic CAT. All patients had at least 6 months follow up from the initial visit. Interventions included RT, systemic CAT, and prednisone. The main outcome measured was prednisone intake. Secondary outcomes were complete remission (CR) and partial remission (PR).
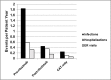
Results: 40 patients were included in the study. All initially received prednisone and at least 1 systemic CAT. 13/40 eventually went on to receive RT, while 27/40 remained on CAT (CAT-only). Patients in the RT group, pre-RT, had a median prednisone intake of 658.57 mg/month. Rituximab treatment significantly reduced this to 177.22 mg/month (p = 0.002). Median prednisone intake of the CAT-only group was 141.33 mg/month. This was significantly less than Pre-RT (p = 0.01) and on par with Post-RT intake (p = 0.58). 54% of patients in the RT group and 64% of those in the CAT-only group achieved CR. All patients in the RT group and 96% of those in the CAT-only group achieved at least PR.
Conclusions: 32.5% of our patients with moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris failed prednisone and traditional CAT treatment and required rituximab therapy. Rituximab reduced the monthly prednisone intake in these patients by 73%. This suggests that a subset of patients with moderate to severe pemphigus may benefit from early institution of rituximab therapy. Rituximab significantly reduces the monthly prednisone requirement among CAT-resistant pemphigus vulgaris patients to levels on par with CAT-responsive patients.
Conflict of interest statement
I would like to affirm that I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: Dr. Hall serves as consultant for and has received research grant support from Stiefel- a GSK Company and Syntimmune. He is a member of the data and safety monitoring board for Roche International, a member of the Eli Lilly Pemphigus Advisory Board and a consultant for Incyte and Principia. Dr. Cardones has received research grant support from Pfizer and is a consultant for Syntimmune. She is also a site investigator for Gilead. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with brief, high-dose intravenous glucocorticoids.Arch Dermatol. 1996 Dec;132(12):1435-9. Arch Dermatol. 1996. PMID: 8961871
-
Treatment of Pemphigus Vulgaris and Foliaceus with Adjuvant Rituximab Compared to Immunosuppression Alone: Real-Life Experience.Dermatology. 2021;237(2):179-184. doi: 10.1159/000508788. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Dermatology. 2021. PMID: 32756069
-
Efficacy and safety of cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, and cyclosporine (ciclosporin) as adjuvant drugs in pemphigus vulgaris.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007;8(2):85-92. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200708020-00004. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17428113
-
Rituximab: A Review in Pemphigus Vulgaris.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020 Feb;21(1):149-156. doi: 10.1007/s40257-019-00497-9. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31838645 Review.
-
Rituximab in childhood pemphigus vulgaris: a long-term follow-up case and review of the literature.Dermatology. 2010 Aug;221(1):13-6. doi: 10.1159/000287254. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Dermatology. 2010. PMID: 20389028 Review.
Cited by
-
Real world evidence: Patients with refractory pemphigus treated with Rituximab.Metabol Open. 2021 Oct 20;12:100142. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100142. eCollection 2021 Dec. Metabol Open. 2021. PMID: 34746731 Free PMC article.
-
Off-Label Uses of Rituximab in Dermatology.Curr Dermatol Rep. 2022;11(4):209-220. doi: 10.1007/s13671-022-00375-4. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36217351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the Clinical Efficacy of Rituximab Infusion and Dexamethasone-Cyclophosphamide Pulse Therapy and Their Effect on Serum Th1, Th2, and Th17 Cytokines in Pemphigus Vulgaris-A Prospective, Nonrandomized, Comparative Pilot Study.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2024 Apr 29;15(3):464-472. doi: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_558_23. eCollection 2024 May-Jun. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2024. PMID: 38845632 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective analysis of pemphigus vulgaris patients: Demographics, diagnosis, co-morbid diseases and treatment modalities used.North Clin Istanb. 2020 Nov 20;7(6):597-602. doi: 10.14744/nci.2020.37039. eCollection 2020. North Clin Istanb. 2020. PMID: 33381700 Free PMC article.
-
Review of an Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody for the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases of the Skin.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):247-273. doi: 10.1007/s40257-022-00751-7. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36630066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

