Dexamethasone counteracts hepatic inflammation and oxidative stress in cholestatic rats via CAR activation
- PMID: 30252871
- PMCID: PMC6155538
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204336
Dexamethasone counteracts hepatic inflammation and oxidative stress in cholestatic rats via CAR activation
Abstract
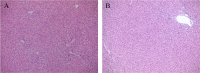
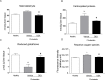
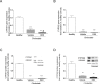
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are currently used for the therapeutic management of cholestatic diseases, but their use and molecular mechanism remain controversial. The aims of this study were 1) to assess the therapeutic effect of a 2-week treatment with the GC dexamethasone on hepatic damage in bile duct-ligated rats; 2) to investigate its effect on the activation of the nuclear receptors (NRs) pregnane X receptor (PXR), constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) and GC receptor (GR), and NF-kB, as well as on oxidative stress and bile acid (BA) hepatic composition. Cholestasis was induced by ligation of bile duct (BDL animals) in 16 male Wistar-Kyoto rats, and eight of them were daily treated by oral gavage with 0.125 mg/ml/kg DEX for 14 days. Eight Sham-operated rats were used as controls. Severity of cholestasis was assessed histologically and on plasma biochemical parameters. The nuclear expression of NF-kB (p65), GR, PXR and CAR was measured in hepatic tissue by Western Blot. Oxidative stress was evaluated by measuring malondialdehyde, carbonylated proteins, GHS and ROS content in rat livers. LC-MS was used to measure the plasma and liver concentration of 7 BAs. Histological findings and a significant drop in several markers of inflammation (p65 nuclear translocation, mRNA expressions of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) showed that DEX treatment reversed cholestasis-induced inflammation, and similar results have been obtained with oxidative stress markers. The nuclear expression of p65 and CAR were inversely correlated, with the latter increasing significantly after DEX treatment (p<0.01 vs vehicle). Hepatic BA levels tended to drop in the untreated cholestatic rats, whereas they were similar to those of healthy rats in DEX-treated animals. Plasma BAs decreased significantly in DEX-treated animals with respect to untreated cholestatic rats. In conclusion, DEX reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in BDL rats, and probably CAR is responsible for this effect. Therefore, this NR represents a promising pharmacological target for managing cholestatic and inflammatory liver diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
SDM received funding from the commercial source "Gilead Inc." This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Ribes diacanthum Pall modulates bile acid homeostasis and oxidative stress in cholestatic mice by activating the SIRT1/FXR and Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 27;342:119400. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119400. Epub 2025 Jan 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39864603
-
Nuclear receptors constitutive androstane receptor and pregnane X receptor ameliorate cholestatic liver injury.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 8;102(6):2063-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409794102. Epub 2005 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15684063 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor modulate differently CYP3A-mediated metabolism in early- and late-stage cholestasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Nov 14;23(42):7519-7530. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7519. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29204052 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptors as therapeutic targets in cholestatic liver diseases.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;156(1):7-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00030.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19133988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PXR- and CAR-mediated herbal effect on human diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1859(9):1121-1129. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.02.009. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26906544 Review.
Cited by
-
Jekyll and Hyde: nuclear receptors ignite and extinguish hepatic oxidative milieu.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Oct;32(10):790-802. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2021.07.009. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34481730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of CAR and PXR Expression in Health and Disease.Cells. 2020 Oct 31;9(11):2395. doi: 10.3390/cells9112395. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33142929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the possible mechanisms of pirfenidone to be targeted as a promising anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, anti-oxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-tumor, and/or anti-SARS-CoV-2.Life Sci. 2022 Nov 15;309:121048. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121048. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36209833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of brown algae Sargassum boveanum on bile duct-ligated cholestasis in rats are mediated by modulating NF-κB/TNF-α and Nrf2/HO-1 gene expression.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2023 Sep-Oct;13(5):513-530. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2023.21970. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2023. PMID: 38089420 Free PMC article.
-
Grape seed meal by-product is able to counteract oxidative stress induced by lipopolysaccharide and dextran sulphate in IPEC cells and piglets after weaning.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 13;18(4):e0283607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283607. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37053301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Courtois A, Payen L, Guillouzo A, Fardel O. Up-regulation of multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) expression in rat hepatocytes by dexamethasone. FEBS Lett. 1999;459:381–385. - PubMed
-
- Kubitz R, Wettstein M, Warskulat U, Häussinger D. Regulation of the multidrug resistance protein 2 in the rat liver by lipopolysaccharide and dexamethasone. Gastroenterology. 1999;116:401–410. - PubMed
-
- Turncliff RZ, Meier PJ, Brouwer KL. Effect of dexamethasone treatment on the expression and function of transport proteins in sandwich-cultured rat hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004;32:834–839. - PubMed
-
- Pascussi JM, Gerbal-Chaloin S, Fabre JM, Maurel P, Vilarem MJ. Dexamethasone enhances constitutive androstane receptor expression in human hepatocytes: Consequences on cytochrome P450 gene regulation. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;58:1441–1450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

