Characterization of zebrafish (Danio rerio) muscle ankyrin repeat proteins reveals their conserved response to endurance exercise
- PMID: 30252882
- PMCID: PMC6155536
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204312
Characterization of zebrafish (Danio rerio) muscle ankyrin repeat proteins reveals their conserved response to endurance exercise
Abstract
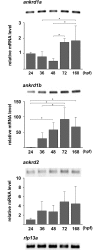
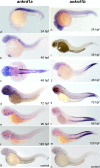
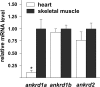
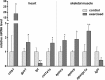
Muscle proteins with ankyrin repeats (MARPs) ANKRD1 and ANKRD2 are titin-associated proteins with a putative role as transcriptional co-regulators in striated muscle, involved in the cellular response to mechanical, oxidative and metabolic stress. Since many aspects of the biology of MARPs, particularly exact mechanisms of their action, in striated muscle are still elusive, research in this field will benefit from novel animal model system. Here we investigated the MARPs found in zebrafish for protein structure, evolutionary conservation, spatiotemporal expression profiles and response to increased muscle activity. Ankrd1 and Ankrd2 show overall moderate conservation at the protein level, more pronounced in the region of ankyrin repeats, motifs indispensable for their function. The two zebrafish genes, ankrd1a and ankrd1b, counterparts of mammalian ANKRD1/Ankrd1, have different expression profiles during first seven days of development. Mild increase of ankrd1a transcript levels was detected at 72 hpf (1.74±0.24 fold increase relative to 24 hpf time point), while ankrd1b expression was markedly upregulated from 24 hpf onward and peaked at 72 hpf (92.18±36.95 fold increase relative to 24 hpf time point). Spatially, they exhibited non-overlapping expression patterns during skeletal muscle development in trunk (ankrd1a) and tail (ankrd1b) somites. Expression of ankrd2 was barely detectable. Zebrafish MARPs, expressed at a relatively low level in adult striated muscle, were found to be responsive to endurance exercise training consisting of two bouts of 3 hours of forced swimming daily, for five consecutive days. Three hours after the last exercise bout, ankrd1a expression increased in cardiac muscle (6.19±5.05 fold change), while ankrd1b and ankrd2 were upregulated in skeletal muscle (1.97±1.05 and 1.84±0.58 fold change, respectively). This study provides the foundation to establish zebrafish as a novel in vivo model for further investigation of MARPs function in striated muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ankrd2 in Mechanotransduction and Oxidative Stress Response in Skeletal Muscle: New Cues for the Pathogenesis of Muscular Laminopathies.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Jul 24;2019:7318796. doi: 10.1155/2019/7318796. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31428229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The stress responsive gene ankrd1a is dynamically regulated during skeletal muscle development and upregulated following cardiac injury in border zone cardiomyocytes in adult zebrafish.Gene. 2021 Aug 5;792:145725. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145725. Epub 2021 May 16. Gene. 2021. PMID: 34010705
-
Probing muscle ankyrin-repeat protein (MARP) structure and function.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014 Sep;297(9):1615-29. doi: 10.1002/ar.22968. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014. PMID: 25125175 Free PMC article.
-
Obscurin is required for the lateral alignment of striated myofibrils in zebrafish.Dev Dyn. 2006 Aug;235(8):2018-29. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20812. Dev Dyn. 2006. PMID: 16779859
-
The enigmatic role of the ankyrin repeat domain 1 gene in heart development and disease.Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(7):811-21. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.082655am. Int J Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18956313 Review.
Cited by
-
Pilot Study on the Profiling and Functional Analysis of mRNA, miRNA, and lncRNA in the Skeletal Muscle of Mongolian Horses, Xilingol Horses, and Grassland-Thoroughbreds.Animals (Basel). 2025 Apr 13;15(8):1123. doi: 10.3390/ani15081123. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281957 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-11 signaling promotes cellular reprogramming and limits fibrotic scarring during tissue regeneration.Sci Adv. 2021 Sep 10;7(37):eabg6497. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abg6497. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34516874 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal serum biomarker screening identifies malate dehydrogenase 2 as candidate prognostic biomarker for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020 Apr;11(2):505-517. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12517. Epub 2019 Dec 27. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020. PMID: 31881125 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise and Asthma.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1228:369-380. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1792-1_25. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32342471 Review.
-
Ankrd2 in Mechanotransduction and Oxidative Stress Response in Skeletal Muscle: New Cues for the Pathogenesis of Muscular Laminopathies.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Jul 24;2019:7318796. doi: 10.1155/2019/7318796. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31428229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zou Y, Evans S, Chen J, Kuo HC, Harvey RP, Chien KR. CARP, a cardiac ankyrin repeat protein, is downstream in the Nkx2-5 homeobox gene pathway. Development. 1997;124(4):793–804. Epub 1997/02/01. . - PubMed
-
- Ishiguro N, Baba T, Ishida T, Takeuchi K, Osaki M, Araki N, et al. Carp, a cardiac ankyrin-repeated protein, and its new homologue, Arpp, are differentially expressed in heart, skeletal muscle, and rhabdomyosarcomas. Am J Pathol. 2002;160(5):1767–78. Epub 2002/05/10. 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61123-6 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC1850855. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

