The trypanocidal benzoxaborole AN7973 inhibits trypanosome mRNA processing
- PMID: 30252911
- PMCID: PMC6173450
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007315
The trypanocidal benzoxaborole AN7973 inhibits trypanosome mRNA processing
Abstract
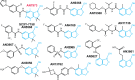
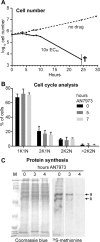
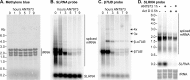
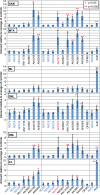
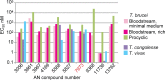
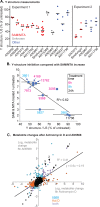
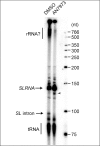
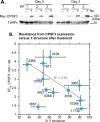
Kinetoplastid parasites-trypanosomes and leishmanias-infect millions of humans and cause economically devastating diseases of livestock, and the few existing drugs have serious deficiencies. Benzoxaborole-based compounds are very promising potential novel anti-trypanosomal therapies, with candidates already in human and animal clinical trials. We investigated the mechanism of action of several benzoxaboroles, including AN7973, an early candidate for veterinary trypanosomosis. In all kinetoplastids, transcription is polycistronic. Individual mRNA 5'-ends are created by trans splicing of a short leader sequence, with coupled polyadenylation of the preceding mRNA. Treatment of Trypanosoma brucei with AN7973 inhibited trans splicing within 1h, as judged by loss of the Y-structure splicing intermediate, reduced levels of mRNA, and accumulation of peri-nuclear granules. Methylation of the spliced leader precursor RNA was not affected, but more prolonged AN7973 treatment caused an increase in S-adenosyl methionine and methylated lysine. Together, the results indicate that mRNA processing is a primary target of AN7973. Polyadenylation is required for kinetoplastid trans splicing, and the EC50 for AN7973 in T. brucei was increased three-fold by over-expression of the T. brucei cleavage and polyadenylation factor CPSF3, identifying CPSF3 as a potential molecular target. Molecular modeling results suggested that inhibition of CPSF3 by AN7973 is feasible. Our results thus chemically validate mRNA processing as a viable drug target in trypanosomes. Several other benzoxaboroles showed metabolomic and splicing effects that were similar to those of AN7973, identifying splicing inhibition as a common mode of action and suggesting that it might be linked to subsequent changes in methylated metabolites. Granule formation, splicing inhibition and resistance after CPSF3 expression did not, however, always correlate and prolonged selection of trypanosomes in AN7973 resulted in only 1.5-fold resistance. It is therefore possible that the modes of action of oxaboroles that target trypanosome mRNA processing might extend beyond CPSF3 inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: Yvonne Freund was employed by Anacor Pharmaceuticals. Benzoxaboroles were supplied by Anacor Pharmaceuticals (YF) which was later taken over by Pfizer. This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS Pathogens policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

