Relationship between three commonly used non-invasive fibrosis biomarkers and improvement in fibrosis stage in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 30253043
- PMCID: PMC6433535
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.13974
Relationship between three commonly used non-invasive fibrosis biomarkers and improvement in fibrosis stage in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
Background & aims: Non-invasive biomarkers are needed for monitoring changes in liver histology in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Obeticholic acid (OCA) was shown to improve fibrosis in patients with NASH in the FLINT trial; a post hoc analysis of these data was performed to determine the relationship between 3 non-invasive fibrosis markers and liver fibrosis improvement.
Methods: In the Phase 2b FLINT trial, patients were randomised (1:1) to receive 25 mg OCA or placebo once daily for 72 weeks. Aspartate aminotransferase:platelet ratio index (APRI), fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease fibrosis score (NFS) were evaluated in serum at baseline and weeks 24, 48, 72 and 96. Liver biopsies were obtained at baseline and 72 weeks.
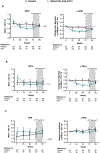
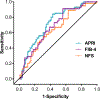
Results: In patients with fibrosis improvement at week 24, scores were reduced by a median of 34% for APRI, 10% for FIB-4 and 4% for NFS. Reductions in APRI (P = 0.015) and FIB-4 (P = 0.036), but not NFS (P = 0.201) at week 24, significantly correlated with ≥1-stage improvement in histologic fibrosis at week 72. Reductions in APRI at week 72 were significantly correlated with fibrosis improvement at week 72 (P = 0.012). Patients receiving OCA had significant reductions in all markers compared with patients receiving placebo at week 72 [APRI and FIB-4 (P < 0.0001); NFS (P < 0.05)].
Conclusions: Readily available non-invasive markers may predict improvement in liver fibrosis in patients with NASH. Upon external confirmation and further refinement in larger populations, these markers may serve as surrogate endpoints in NASH clinical trials.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01265498.
Keywords: biomarkers; fibrosis; non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; non-invasive.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interests:
NC received consulting fees from AbbVie Inc., Domain Therapeutics, Afimmune, Eli Lilly and Company, Cempra, Shire, Axovant, Ardelyx, NuSirt Biopharma, and Tobira (Allergan) Therapeutics, Inc., and grant/research support from Galectin Therapeutics Inc., Cumberland, Gilead Sciences, Inc., and Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc. MFA received consulting fees from BHV Pharma, Inc., and TaiwanJ Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd. and grant/research support from Allergan, Arisaph Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Boehringer-Ingelheim GmbH, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Conatus Pharmaceuticals Inc., Exalenz Bioscience Ltd., Galectin Therapeutics Inc., Galmed Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Genfit Corp., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Immuron, Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc., NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., NIH/NIDDK, Shire, TaiwanJ Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd., and Tobira Therapeutics, Inc. MFA has also received speaker fees from Alexion Pharma GmbH and advisory/review panel fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Celgene Corporation, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., and Pfizer Inc. RL received advisory/review panel fees from Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Galmed Pharmaceuticals Ltd., and Tobira Therapeutics, Inc., and consulting fees from Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Celgene Corporation, Corgenix, DeuteRx, Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Zafgen Inc. RL also received grant/research support from Adheron Therapeutics, Inc., AGA Pharma & Supplements SL, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Ltd., Immuron, KineMed, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., and Promedior, Inc. KVK received advisory/review panel fees from AbbVie Inc., Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Trio Health, and Verlyx Pharma Inc. and grant/research support from AbbVie Inc., Evidera, Galectin Therapeutics Inc., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Immuron, Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Tobira Therapeutics, Inc., and Trio Health. KVK has also received speaker fees from Gilead Sciences, Inc., and Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc. AJM has nothing to disclose. SD received consulting fees from Fresenius Kabi. BAN-T received advisory/review panel fees from Allergan, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Conatus Pharmaceuticals Inc., Galmed Pharmaceuticals, Ltd., Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Nimbus Therapeutics, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Pfizer Inc., Receptos Services, LLC, and Zafgen Inc. and consulting fees from Medimmune. NT received advisory/review panel fees from Biotest Pharmaceuticals Corporation and Eisai Co., Ltd. and consulting fees from Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Cocrystal Pharma, Inc., and Merck & Co., Inc. NT also received grant/research support from AbbVie Inc., Biotest Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Eisai Co., Ltd., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc. BF is an employee of Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc. RS is an employee of Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and receives stock ownership. DS is an employee of Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and receives stock ownership. AJS received advisory/review panel fees from Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Exalenz Bioscience Ltd., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Genfit Corp., Ikaria, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, and Pfizer Inc. and consulting fees from Echosens, Genentech, Inc., HemoShear Therapeutics, LLC, JD Pharma Consultants Pvt. Ltd., Nimbus Therapeutics, Merck & Co., Inc., Salix Pharmaceuticals, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd., and Zafgen Inc. AJS also received grant/research support from Galmed Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Genentech, Inc., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Ikaria, Inc., Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Salix Pharmaceuticals, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd., and Tobira Therapeutics, Inc., and contracting fees from Elsevier B.V. and UpToDate, Inc. AJS also holds a management position at Sanyal Biotechnology and has stock options in Genfit, HemoShear, Exalenz, and Galmed.
Figures


Comment in
-
Reading the stars for hepatic fibrosis or how to predict the severity of liver disease in patients with NASH.Liver Int. 2019 May;39(5):812-814. doi: 10.1111/liv.13999. Liver Int. 2019. PMID: 31020772 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Non-invasive evaluation of response to obeticholic acid in patients with NASH: Results from the REGENERATE study.J Hepatol. 2022 Mar;76(3):536-548. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.10.029. Epub 2021 Nov 15. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34793868
-
Factors Associated With Histologic Response in Adult Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Gastroenterology. 2019 Jan;156(1):88-95.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.09.021. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30222962 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Noninvasive Fibrosis Models to Detect Change in Fibrosis Stage.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Aug;17(9):1877-1885.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.12.031. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30616027 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Clinical prediction rules and blood-based biomarkers.J Hepatol. 2018 Feb;68(2):305-315. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.013. Epub 2017 Dec 2. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29154965 Review.
-
Noninvasive biomarkers in predicting nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and assessing liver fibrosis: systematic review and meta-analysis.Panminerva Med. 2021 Dec;63(4):508-518. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.20.04171-3. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Panminerva Med. 2021. PMID: 33165307
Cited by
-
Role of noninvasive tests in the prognostication of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2025 Feb;31(Suppl):S51-S75. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0246. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 38934108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Testosterone Replacement Therapy Can Improve a Biomarker of Liver Fibrosis in Hypogonadal Men: A Subanalysis of a Prospective Randomized Controlled Study in Japan (EARTH Study).World J Mens Health. 2025 Jul;43(3):661-668. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.240066. Epub 2024 Oct 14. World J Mens Health. 2025. PMID: 39434391 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Invasive Serum Markers of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Fibrosis: Potential Tools for Detecting Patients with Cardiovascular Disease.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Sep 24;25(9):344. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2509344. eCollection 2024 Sep. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39355605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of bariatric surgery on fatty liver disease in obese patients: A prospective one year follow-up study.Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2022 May;166(2):195-203. doi: 10.5507/bp.2021.021. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2022. PMID: 33885048
-
Is the grade of ballooned hepatocytes a significant risk factor for rapid progression of hepatic fibrosis in patients with NAFLD?J Gastroenterol. 2019 May;54(5):474-475. doi: 10.1007/s00535-019-01573-x. Epub 2019 Mar 26. J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30915535 No abstract available.
References
-
- Charlton MR, Burns JM, Pedersen RA, Watt KD, Heimbach JK, Dierkhising RA. Frequency and outcomes of liver transplantation for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in the United States. Gastroenterology 2011;141(4):1249–1253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

