Oxytocin in metabolic homeostasis: implications for obesity and diabetes management
- PMID: 30253045
- PMCID: PMC7888317
- DOI: 10.1111/obr.12757
Oxytocin in metabolic homeostasis: implications for obesity and diabetes management
Abstract
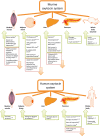
Oxytocin was once understood solely as a neuropeptide with a central role in social bonding, reproduction, parturition, lactation and appetite regulation. Recent evidence indicates that oxytocin enhances glucose uptake and lipid utilization in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle, suggesting that dysfunction of the oxytocin system could underlie the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and dyslipidaemia. Murine studies revealed that deficiencies in oxytocin signalling and oxytocin receptor expression lead to obesity despite normal food intake, motor activity and increased leptin levels. In addition, plasma oxytocin concentration is notably lower in obese individuals with diabetes, which may suggest an involvement of the oxytocin system in the pathogenesis of cardiometabolic disease. More recently, small scale studies demonstrated that intranasal administration of oxytocin was associated with significant weight loss as well as improvements in insulin sensitivity and pancreatic β-cell responsivity in human subjects. The multi-pronged effects of oxytocin signalling on improving peripheral insulin sensitivity, pancreatic function and lipid homeostasis strongly suggest a role for this system as a therapeutic target in obesity and diabetes management. The complexity of obesity aetiology and the pathogenesis of obesity-related metabolic complications underscore the need for a systems approach to better understand the role of oxytocin in metabolic function.
Keywords: beta cell function; glucose metabolism; insulin sensitivity; lipid metabolism.
© 2018 The Authors. Obesity Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of World Obesity Federation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Kamm O, Aldrich TB, Grote IW, Rowe LW, Bugbee EP. The active principles of the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland.1i. The demonstration of the presence of two active principles. Ii. The separation of the two principles and their concentration in the form of potent solid preparations. J Am Chem Soc. 1928; 50: 573–601.
-
- Pinkerton JHM. Advances in Oxytocin Research. Pergamon Press: Oxford, 1965.
-
- Burt RL, Leake NH, Dannenburg WN. Effect of synthetic oxytocin on plasma nonesterified fatty acids, triglycerides, and blood glucose. Obstet Gynecol. 1963; 21: 708–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

