Centella asiatica attenuates hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction and improves memory and executive function in β-amyloid overexpressing mice
- PMID: 30253196
- PMCID: PMC6242741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.09.002
Centella asiatica attenuates hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction and improves memory and executive function in β-amyloid overexpressing mice
Abstract
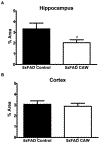
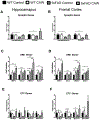
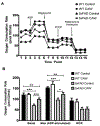
Centella asiatica is a medicinal plant used to enhance memory. We have previously shown that a water extract of Centella asiatica (CAW) attenuates β-amyloid (Aβ)-induced spatial memory deficits in mice and improves neuronal health. Yet the effect of CAW on other cognitive domains remains unexplored as does its in vivo mechanism of improving Aβ-related cognitive impairment. This study investigates the effects of CAW on learning, memory and executive function as well as mitochondrial function and antioxidant response in the 5xFAD model of Aβ accumulation. Seven month old 5xFAD female mice were treated with CAW (2 mg/mL) in their drinking water for two weeks prior to behavioral testing. Learning, memory and executive function were assessed using the object location memory task (OLM), conditioned fear response (CFR) and odor discrimination reversal learning (ODRL) test. Mitochondrial function was profiled using the Seahorse XF platform in hippocampal mitochondria isolated from these animals and tissue was harvested for assessment of mitochondrial, antioxidant and synaptic proteins. CAW improved performance in all behavioral tests in the 5xFAD but had no effect on WT animals. Hippocampal mitochondrial function was improved and hippocampal and cortical expression of mitochondrial genes was increased in CAW-treated 5xFAD mice. Gene expression of the transcription factor NRF2, as well as its antioxidant target enzymes, was also increased with CAW treatment in both WT and 5xFAD mice. CAW treatment also decreased Aβ-plaque burden in the hippocampus of treated 5xFAD mice but had no effect on plaques in the cortex. These data show that CAW can improve many facets of Aβ-related cognitive impairment in 5xFAD mice. Oral treatment with CAW also attenuates hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction in these animals. Because mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress accompany cognitive impairment in many pathological conditions beyond Alzheimer's disease, this suggests potentially broad therapeutic utility of CAW.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Beta amyloid; Executive function; Mitochondrial function.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Ashendorf L, McCaffrey RJ. (2008). “Exploring age-related decline on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test.” Clin Neuropsychol 22(2): 262–272. - PubMed
-
- Assini F, Duzzioni M, Takahashi RN. (2009). “Object location memory in mice: pharmacological validation and further evidence of hippocampal CA1 participation.” Behav Brain Res 204(1): 206–211. - PubMed
-
- Association., A. s. (2017). “Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures.” Alzheimer’s and Dementia 13: 325–373.
-
- Baloyannis SJ (2009). “Dendritic pathology in Alzheimer’s disease.” J Neurol Sci. 283(1–2): 153–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

