Genome-wide analyses of genes encoding FK506-binding proteins reveal their involvement in abiotic stress responses in apple
- PMID: 30253753
- PMCID: PMC6156878
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-5097-8
Genome-wide analyses of genes encoding FK506-binding proteins reveal their involvement in abiotic stress responses in apple
Abstract
Background: The FK506-binding proteins (FKBPs) play diverse roles in numerous critical processes for plant growth, development, and abiotic stress responses. However, the FKBP gene family in the important fruit crop apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) has not been studied as thoroughly as in other species. Our research objective was to investigate the mechanisms by which apple FKBPs enable apple plants to tolerate the effects of abiotic stresses.
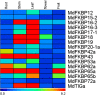
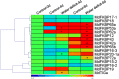
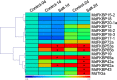
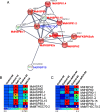
Results: Using bioinformatics-based methods, RT-PCR, and qRT-PCR technologies, we identified 38 FKBP genes and cloned 16 of them in the apple genome. The phylogenetic analysis revealed three major groups within that family. The results from sequence alignments, 3-D structures, phylogenetics, and analyses of conserved domains indicated that apple FKBPs are highly and structurally conserved. Furthermore, genomics structure analysis showed that those genes are also highly and structurally conserved in several other species. Comprehensive qRT-PCR analysis found various expression patterns for MdFKBPs in different tissues and in plant responses to water-deficit and salt stresses. Based on the results from interaction network and co-expression analyses, we determined that the pairing in the MdFKBP62a/MdFKBP65a/b-mediated network is involved in water-deficit and salt-stress signaling, both of which are uniformly up-regulated through interactions with heat shock proteins in apple.
Conclusions: These results provide new insight for further study of FKBP genes and their functions in abiotic stress response and multiple metabolic and physiological processes in apple.
Keywords: Apple; Drought stress; Expression analysis; FKBP gene family; Genome-wide; Salt stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

