Genetically enhancing the expression of chemokine domain of CX3CL1 fails to prevent tau pathology in mouse models of tauopathy
- PMID: 30253780
- PMCID: PMC6154806
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-018-1310-6
Genetically enhancing the expression of chemokine domain of CX3CL1 fails to prevent tau pathology in mouse models of tauopathy
Abstract
Background: Fractalkine (CX3CL1) and its receptor (CX3CR1) play an important role in regulating microglial function. We have previously shown that Cx3cr1 deficiency exacerbated tau pathology and led to cognitive impairment. However, it is still unclear if the chemokine domain of the ligand CX3CL1 is essential in regulating neuronal tau pathology.
Methods: We used transgenic mice lacking endogenous Cx3cl1 (Cx3cl1-/-) and expressing only obligatory soluble form (with only chemokine domain) and lacking the mucin stalk of CX3CL1 (referred to as Cx3cl1105Δ mice) to assess tau pathology and behavioral function in both lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and genetic (hTau) mouse models of tauopathy.
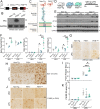
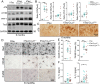
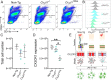
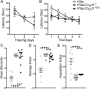
Results: First, increased basal tau levels accompanied microglial activation in Cx3cl1105Δ mice compared to control groups. Second, increased CD45+ and F4/80+ neuroinflammation and tau phosphorylation were observed in LPS, hTau/Cx3cl1-/-, and hTau/Cx3cl1105Δ mouse models of tau pathology, which correlated with impaired spatial learning. Finally, microglial cell surface expression of CX3CR1 was reduced in Cx3cl1105Δ mice, suggesting enhanced fractalkine receptor internalization (mimicking Cx3cr1 deletion), which likely contributes to the elevated tau pathology.
Conclusions: Collectively, our data suggest that overexpression of only chemokine domain of CX3CL1 does not protect against tau pathology.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; CX3CL1; CX3CR1; Microglia; Neuroinflammation; Tau; Tauopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All animal experiments performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation and the University of New Mexico.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
-
Fractalkine overexpression suppresses tau pathology in a mouse model of tauopathy.Neurobiol Aging. 2013 Jun;34(6):1540-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.12.011. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Neurobiol Aging. 2013. PMID: 23332170 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of tau pathology by the microglial fractalkine receptor.Neuron. 2010 Oct 6;68(1):19-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.023. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20920788 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive microglia drive tau pathology and contribute to the spreading of pathological tau in the brain.Brain. 2015 Jun;138(Pt 6):1738-55. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv081. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25833819 Free PMC article.
-
CX3CL1/CX3CR1 in Alzheimer's Disease: A Target for Neuroprotection.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:8090918. doi: 10.1155/2016/8090918. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27429982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Chemokines in the Development and Progression of Alzheimer's Disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2022 Sep;72(9):1929-1951. doi: 10.1007/s12031-022-02047-1. Epub 2022 Jul 12. J Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35821178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CX3CL1 Regulation of Gliosis in Neuroinflammatory and Neuroprotective Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 23;26(3):959. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030959. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanism and potential therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Sep 22;8(1):359. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01588-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37735487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease: a Key Player in the Transition Between Homeostasis and Pathogenesis.Neurotherapeutics. 2022 Jan;19(1):186-208. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01179-3. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Neurotherapeutics. 2022. PMID: 35286658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Jul;58(7):3388-3404. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02348-3. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33713018 Review.
References
-
- Harrison JK, Jiang Y, Chen S, Xia Y, Maciejewski D, McNamara RK, Streit WJ, Salafranca MN, Adhikari S, Thompson DA, et al. Role for neuronally derived fractalkine in mediating interactions between neurons and CX3CR1-expressing microglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:10896–10901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.18.10896. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Imai T, Hieshima K, Haskell C, Baba M, Nagira M, Nishimura M, Kakizaki M, Takagi S, Nomiyama H, Schall TJ, Yoshie O. Identification and molecular characterization of fractalkine receptor CX3CR1, which mediates both leukocyte migration and adhesion. Cell. 1997;91:521–530. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80438-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garton KJ, Gough PJ, Blobel CP, Murphy G, Greaves DR, Dempsey PJ, Raines EW. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme (ADAM17) mediates the cleavage and shedding of fractalkine (CX3CL1) J Biol Chem. 2001;276:37993–38001. - PubMed
-
- Hundhausen C, Misztela D, Berkhout TA, Broadway N, Saftig P, Reiss K, Hartmann D, Fahrenholz F, Postina R, Matthews V, et al. The disintegrin-like metalloproteinase ADAM10 is involved in constitutive cleavage of CX3CL1 (fractalkine) and regulates CX3CL1-mediated cell-cell adhesion. Blood. 2003;102:1186–1195. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3775. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21NS093442/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS078501/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NIRG-11-204995/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- P20 GM109089/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023012/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS083704/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY022358/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG050409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY022358/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG051495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- W81XWH-13 MRPRA-CSRA/U.S. Department of Defense
- R21 NS093442/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS078501/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS047804/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- SC1 GM095426/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS077089/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG023012 and RF1AG051495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- SC1GM095426/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS083704/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AHAF0311/American Health Assistance Foundation
- R21 NS077089/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR001108/Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute
- F31AG050409-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

