HO Endonuclease-Initiated Recombination in Yeast Meiosis Fails To Promote Homologous Centromere Pairing and Is Not Constrained To Utilize the Dmc1 Recombinase
- PMID: 30254180
- PMCID: PMC6222578
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.118.200641
HO Endonuclease-Initiated Recombination in Yeast Meiosis Fails To Promote Homologous Centromere Pairing and Is Not Constrained To Utilize the Dmc1 Recombinase
Abstract
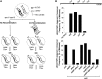
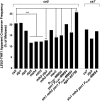
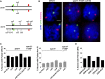
Crossover recombination during meiosis is accompanied by a dramatic chromosome reorganization. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the onset of meiotic recombination by the Spo11 transesterase leads to stable pairwise associations between previously unassociated homologous centromeres followed by the intimate alignment of homologous axes via synaptonemal complex (SC) assembly. However, the molecular relationship between recombination and global meiotic chromosome reorganization remains poorly understood. In budding yeast, one question is why SC assembly initiates earliest at centromere regions while the DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) that initiate recombination occur genome-wide. We targeted the site-specific HO endonuclease to various positions on S. cerevisiae's longest chromosome in order to ask whether a meiotic DSB's proximity to the centromere influences its capacity to promote homologous centromere pairing and SC assembly. We show that repair of an HO-mediated DSB does not promote homologous centromere pairing nor any extent of SC assembly in spo11 meiotic nuclei, regardless of its proximity to the centromere. DSBs induced en masse by phleomycin exposure likewise do not promote homologous centromere pairing nor robust SC assembly. Interestingly, in contrast to Spo11, HO-initiated interhomolog recombination is not affected by loss of the meiotic kinase, Mek1, and is not constrained to use the meiosis-specific Dmc1 recombinase. These results strengthen the previously proposed idea that (at least some) Spo11 DSBs may be specialized in activating mechanisms that both 1) reinforce homologous chromosome alignment via homologous centromere pairing and SC assembly, and 2) establish Dmc1 as the primary strand exchange enzyme.
Keywords: HO endonuclease; Spo11; chromosome pairing; meiosis; recombination; synapsis.
Copyright © 2018 Yisehak, MacQueen.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Switching yeast from meiosis to mitosis: double-strand break repair, recombination and synaptonemal complex.Genes Cells. 1997 Aug;2(8):487-98. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1997.1370335.x. Genes Cells. 1997. PMID: 9348039
-
Multiple Pairwise Analysis of Non-homologous Centromere Coupling Reveals Preferential Chromosome Size-Dependent Interactions and a Role for Bouquet Formation in Establishing the Interaction Pattern.PLoS Genet. 2016 Oct 21;12(10):e1006347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006347. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27768699 Free PMC article.
-
Rad51-mediated interhomolog recombination during budding yeast meiosis is promoted by the meiotic recombination checkpoint and the conserved Pif1 helicase.PLoS Genet. 2022 Dec 12;18(12):e1010407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010407. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36508468 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple roles of the Mre11 complex for meiotic recombination.Chromosome Res. 2007;15(5):551-63. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1147-9. Chromosome Res. 2007. PMID: 17674145 Review.
-
Female Meiosis: Synapsis, Recombination, and Segregation in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2018 Mar;208(3):875-908. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300081. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29487146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Turning coldspots into hotspots: targeted recruitment of axis protein Hop1 stimulates meiotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2022 Aug 30;222(1):iyac106. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac106. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35876814 Free PMC article.
-
Meiosis in budding yeast.Genetics. 2023 Oct 4;225(2):iyad125. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad125. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 37616582 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
