BRAF V600E and RET/PTC Promote the Activity of Nuclear Factor-κB, Inflammatory Mediators, and Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Study of 50 Patients in Inner Mongolia
- PMID: 30254191
- PMCID: PMC6180901
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.909205
BRAF V600E and RET/PTC Promote the Activity of Nuclear Factor-κB, Inflammatory Mediators, and Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Study of 50 Patients in Inner Mongolia
Abstract
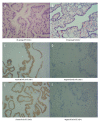
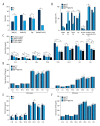
BACKGROUND The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of the BRAF V600E gene mutation and the RET/PTC gene rearrangement in the progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) in 50 patients from Inner Mongolia. MATERIAL AND METHODS Clinical data, blood, and tissue samples were obtained from 50 patients with PTC and ten patients with benign thyroid adenoma. Expression of BRAF V600E, RET/PTC, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand (CXCL)1, CXCL2, C-C motif chemokine ligand (CCL)2, and CCL3 were measured using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), immunohistochemistry, and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). RESULTS Of the 50 patients with PTC, 37 patients expressed the BRAF V600E gene mutation, eight patients expressed RET/PTC, and five patients showed concomitant BRAF V600E and RET/PTC. Time to recurrence for patients with PTC with BRAF V600E was significantly increased compared with patients with concomitant BRAF V600E mutation and RET/PTC rearrangement (P<0.05). Expression of BRAF V600E, RET/PTC, and concomitant expression of BRAF V600E and RET/PTC were significantly associated with patient age and lymph node metastasis (P<0.05). Serum levels of NF-κB, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, TGF-β and CCL3, and tumor tissue levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, TGF-β, CXCL2 and CCL2 in patients with PTC were significantly increased compared with patients with benign thyroid adenoma, before and after surgery (P<0.05). CONCLUSIONS Expression of the BRAF V600E mutation and RET/PTC translocation promoted the activity of NF-κB, expression of inflammatory mediators, and lymph node metastases in patients with PTC.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Concomitant BRAF(V600E) mutation and RET/PTC rearrangement is a frequent occurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Thyroid. 2014 Feb;24(2):254-9. doi: 10.1089/thy.2013.0235. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Thyroid. 2014. PMID: 23806056
-
Correlation Between the Clinicopathological Features of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Complicated with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis, BRAF V600E Gene Mutation, and RET Gene Rearrangement.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2024 Apr;34(4):445-450. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2024.04.445. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2024. PMID: 38576288
-
BRAFV600E and RET/PTC Promote Proliferation and Migration of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells In Vitro by Regulating Nuclear Factor-κB.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Nov 8;23:5321-5329. doi: 10.12659/msm.904928. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 29117154 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that one subset of anaplastic thyroid carcinomas are derived from papillary carcinomas due to BRAF and p53 mutations.Cancer. 2005 Jun 1;103(11):2261-8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21073. Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15880523 Review.
-
BRAF(V600E) and microenvironment in thyroid cancer: a functional link to drive cancer progression.Cancer Res. 2011 Apr 1;71(7):2417-22. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3844. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21447745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Coexistence of Genetic Mutations in Thyroid Carcinoma Predicts Histopathological Factors Associated With a Poor Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 3;10:540238. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.540238. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33240806 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome activation as a link between obesity and thyroid disorders: Implications for an integrated clinical management.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 19;13:959276. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.959276. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36060941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRX5's influence on macrophage polarization and outcome in papillary thyroid cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 May 29;14:1399484. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1399484. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38868535 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL2: a key player in the tumor microenvironment and inflammatory diseases.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Apr 7;25(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03765-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40197328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1β and Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 4;12(7):1791. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071791. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32635472 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hundahl SA, Fleming ID, Fremgen AM, Menck HR. A National Cancer Database Report on 53,856 cases of thyroid carcinoma treated in the U.S., 1985–1995. Cancer. 1998;83(12):2638–48. - PubMed
-
- Yu GP, Li JC, Branovan D, et al. Thyroid cancer incidence and survival in the National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results race/ethnicity groups. Thyroid. 2010;20(5):465–73. - PubMed
-
- Sherman SI, Angelos P, Ball DW, et al. Thyroid carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;361(9356):501–11. - PubMed
-
- Gimm O. Thyroid cancer. Cancer Lett. 2001;163(2):143–56. - PubMed
-
- Marais R, Light Y, Paterson HF, et al. Differential regulation of Raf-1, A-Raf, and B-Raf by oncogenic ras and tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(7):4378–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

