Analysis of extracellular mRNA in human urine reveals splice variant biomarkers of muscular dystrophies
- PMID: 30254196
- PMCID: PMC6156576
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06206-0
Analysis of extracellular mRNA in human urine reveals splice variant biomarkers of muscular dystrophies
Abstract
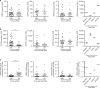
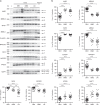
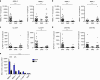
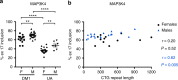
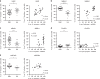
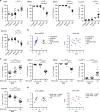
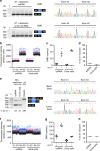
Urine contains extracellular RNA (exRNA) markers of urogenital cancers. However, the capacity of genetic material in urine to identify systemic diseases is unknown. Here we describe exRNA splice products in human urine as a source of biomarkers for the two most common forms of muscular dystrophies, myotonic dystrophy (DM) and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Using a training set, RT-PCR, droplet digital PCR, and principal component regression, we identify ten transcripts that are spliced differently in urine exRNA from patients with DM type 1 (DM1) as compared to unaffected or disease controls, form a composite biomarker, and develop a predictive model that is 100% accurate in our independent validation set. Urine also contains mutation-specific DMD mRNAs that confirm exon-skipping activity of the antisense oligonucleotide drug eteplirsen. Our results establish that urine mRNA splice variants can be used to monitor systemic diseases with minimal or no clinical effect on the urinary tract.
Conflict of interest statement
Massachusetts General Hospital, T.M.W., X.O.B., and L.B. have filed a patent application on the use of urine exRNA to identify markers of muscular dystrophies. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

