Prediagnostic detection of mesothelioma by circulating calretinin and mesothelin - a case-control comparison nested into a prospective cohort of asbestos-exposed workers
- PMID: 30254313
- PMCID: PMC6156219
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32315-3
Prediagnostic detection of mesothelioma by circulating calretinin and mesothelin - a case-control comparison nested into a prospective cohort of asbestos-exposed workers
Abstract
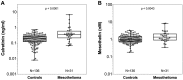
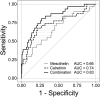
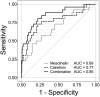
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is strongly associated with a previous asbestos exposure. To improve timely detection of MM in asbestos workers, better screening tools - like minimally-invasive biomarkers - are desirable. Between 2008 and 2018 2,769 patients with benign asbestos-related diseases were recruited to participate in annual screens. Using a nested case-control design the protein markers calretinin and mesothelin were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays in prediagnostic plasma samples of 34 MM cases as well as 136 matched controls from the cohort. Conditional on a pre-defined specificity of 98% for calretinin and 99% for mesothelin the markers reached individual sensitivities of 31% and 23%, respectively, when including the incident cases with samples taken between one and 15 months before diagnosis. The combination of both markers increased the sensitivity to 46% at 98% specificity. Marker complementation increased with earlier sampling. The marker combination improves the sensitivity of the individual markers, indicating a useful complementation and suggesting that additional markers may further improve the performance. This is the first prospective cohort study to evaluate a detection of MM by calretinin and its combination with mesothelin up to about a year before clinical diagnosis. Whether an earlier diagnosis will result in reduced mortality has yet to be demonstrated.
Conflict of interest statement
The IPA has supplied DLD Diagnostika GmbH with the antibodies to produce the Calretinin ELISA kits. In turn, the IPA has received Calretinin ELISA kits at a reduced price and may benefit from future sales of the kits. Otherwise, the individual authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calretinin as a blood-based biomarker for mesothelioma.BMC Cancer. 2017 May 30;17(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3375-5. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28558669 Free PMC article.
-
Mesothelin, Calretinin, and Megakaryocyte Potentiating Factor as Biomarkers of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.Lung. 2019 Oct;197(5):641-649. doi: 10.1007/s00408-019-00244-1. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Lung. 2019. PMID: 31267149
-
Assessment of potential predictors of calretinin and mesothelin to improve the diagnostic performance to detect malignant mesothelioma: results from a population-based cohort study.BMJ Open. 2017 Oct 11;7(10):e017104. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017104. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29025836 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of screening for malignant pleural mesothelioma.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009 Summer;21(2):97-104. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2009.06.007. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009. PMID: 19822280 Review.
-
Malignant Mesothelioma Biomarkers: From Discovery to Use in Clinical Practice for Diagnosis, Monitoring, Screening, and Treatment.Chest. 2017 Jul;152(1):143-149. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.12.004. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Chest. 2017. PMID: 28007619 Review.
Cited by
-
Exhaled Breath Analysis in Diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Feb 10;17(3):1110. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17031110. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32050546 Free PMC article.
-
Follow-up of Soluble Mesothelin-Related Protein Levels in Participants With Asbestos-Related Disorders.Saf Health Work. 2020 Dec;11(4):425-430. doi: 10.1016/j.shaw.2020.07.009. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Saf Health Work. 2020. PMID: 33329908 Free PMC article.
-
[The Current Therapy of Asbestos-Associated Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma - An Expert Consensus Paper].Pneumologie. 2021 Oct;75(10):776-794. doi: 10.1055/a-1404-1562. Epub 2021 May 4. Pneumologie. 2021. PMID: 33946118 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
[Mesothelioma-30 years after the asbestos ban in Germany].Pathologie (Heidelb). 2024 Sep;45(5):305-308. doi: 10.1007/s00292-024-01350-5. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Pathologie (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 39083122 Review. German.
-
Circulating Epigenetic Biomarkers in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State of the Art and critical Evaluation.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 3;10:445. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00445. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32318342 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- IARC IARC monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to man: asbestos. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risk Chem Man. 1977;14:1–106. - PubMed
-
- Dragani, T. A., Colombo, F., Pavlisko, E. N. & Roggli, V. L. Malignant mesothelioma diagnosed at a younger age is associated with heavier asbestos exposure. Carcinogenesis (in press). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

