GlycoPEGylated recombinant factor IX for hemophilia B in context
- PMID: 30254423
- PMCID: PMC6141116
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S121743
GlycoPEGylated recombinant factor IX for hemophilia B in context
Abstract
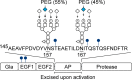
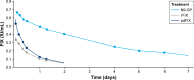
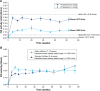
Decisions over hemophilia treatment selection and switching involve balancing many clinical and patient-related factors. The current standard of care for patients with hemophilia B is prophylaxis with plasma-derived or recombinant factor IX (rFIX) concentrates. However, several extended half-life (EHL) rFIX products have recently been developed to improve treatment convenience and clinical outcomes for these patients. Nonacog beta pegol, an rFIX product that combines the FIX protein with a 40 kDa polyethylene glycol moiety, has been evaluated in 115 previously treated patients with hemophilia B (including 25 children) in the paradigm clinical trial program. FIX activity levels and pharmacokinetics were monitored throughout these trials and showed that nonacog beta pegol offers significant pharmacological improvements over standard FIX products. Once-weekly prophylaxis with nonacog beta pegol 40 IU/kg resulted in fewer bleeds in all patients (median annualized bleeding rate of 1.0 across all ages), resolved 90% of target joints, and improved health-related quality of life. No patients developed FIX inhibitors, and there were no thromboembolic events or unexpected safety concerns. Nonacog beta pegol was also safe and effective in the perioperative setting. These findings show that nonacog beta pegol is highly effective, while also offering more convenient dosing than standard FIX products. Nonacog beta pegol represents a significant advance in the current context of treatment for hemophilia B, offering effective management across several treatment modalities and settings, and potentially easing the treatment burden for patients of all ages. Meanwhile, the development of novel treatment strategies, such as gene therapy, anti-tissue factor pathway inhibitor antibodies, and RNA interference therapy, may provide patients with additional therapeutic options, which would require reassessment of the role of EHL products in the future.
Keywords: PEGylated rFIX; extended half-life; long-acting FIX; prophylaxis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure E Santagostino has acted as an advisor or speaker for Bayer, Bioverativ, CSL Behring, Grifols, Kedrion, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer, Roche, Shire, and SOBI. ME Mancuso has acted as a consultant/advisor/speaker for Baxalta/Shire, Bayer HealthCare, CSL Behring, Kedrion, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer, Roche, and SOBI/Biogen. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nonacog beta pegol in previously treated children with hemophilia B: results from an international open-label phase 3 trial.J Thromb Haemost. 2016 Aug;14(8):1521-9. doi: 10.1111/jth.13360. Epub 2016 Jun 22. J Thromb Haemost. 2016. PMID: 27174727 Clinical Trial.
-
Recombinant long-acting glycoPEGylated factor IX (nonacog beta pegol) in haemophilia B: assessment of target joints in multinational phase 3 clinical trials.Haemophilia. 2016 Jul;22(4):507-13. doi: 10.1111/hae.12902. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Haemophilia. 2016. PMID: 26936227 Clinical Trial.
-
Nonacog Beta Pegol: A Review in Haemophilia B.Drugs. 2017 Dec;77(18):2003-2012. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0836-8. Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29124682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-factor consumption for major surgery in haemophilia B with long-acting recombinant glycoPEGylated factor IX.Haemophilia. 2017 Jan;23(1):67-76. doi: 10.1111/hae.13041. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Haemophilia. 2017. PMID: 27480487
-
FIXing postinfusion monitoring: Assay experiences with N9-GP (nonacog beta pegol; Refixia® ; Rebinyn® ).Haemophilia. 2019 Jan;25(1):154-161. doi: 10.1111/hae.13671. Haemophilia. 2019. PMID: 30664825 Review.
Cited by
-
Nonacog beta pegol prophylaxis in children with hemophilia B: safety, efficacy, and neurodevelopmental outcomes for up to 8 years.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2024 Feb 8;8(2):102341. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2024.102341. eCollection 2024 Feb. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 38516633 Free PMC article.
-
The Indian Experience With Nonacog Beta Pegol for the Treatment of Hemophilia B in Children and Adolescents: A Safety and Efficacy Evaluation.Cureus. 2025 Apr 28;17(4):e83158. doi: 10.7759/cureus.83158. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40443617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Srivastava A, Brewer AK, Mauser-Bunschoten EP, et al. Treatment Guidelines Working Group on Behalf of The World Federation of Hemophilia Guidelines for the management of hemophilia. Haemophilia. 2013;19(1):e1–e47. - PubMed
-
- Carcao M. Changing paradigm of prophylaxis with longer acting factor concentrates. Haemophilia. 2014;20(suppl 4):99–105. - PubMed
-
- Franchini M, Frattini F, Crestani S, Bonfanti C. Haemophilia B: current pharmacotherapy and future directions. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2012;13(14):2053–2063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

