PPP5C promotes cell proliferation and survival in human prostate cancer by regulating of the JNK and ERK1/2 phosphorylation
- PMID: 30254472
- PMCID: PMC6140725
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S161280
PPP5C promotes cell proliferation and survival in human prostate cancer by regulating of the JNK and ERK1/2 phosphorylation
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the most common malignancies and a major leading cause of cancer-related deaths in males. And it is necessary to explore new molecular targets to enhance diagnosis and treatment level of the PCa. Serine/threonine protein phosphatase 5 (PPP5C) is a vital molecule that Involve in complex cell physiological activity.
Purpose: The objective of this study was to detecte the expression level of PPP5C in the tissue of prostate cancer patients and further discussed the PPP5C biological function and mechanisms on the PCa.
Methods: The expression level of PPP5C was analyzed by immunohistochemistry and ONCOM-INE datasets. Lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA (shRNA) was constructed to silence the expression of PPP5C in prostate cancer cell. Cell viability and proliferation were measured using MTT and colony formation, and the cell cycle and apoptosis was analyszed by flow cytometry. The changes of downstream protein level and protein phosphorylation level were detected by western blot.
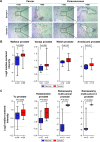
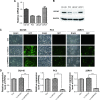
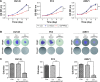
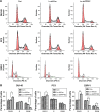
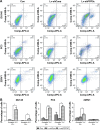
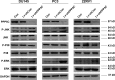
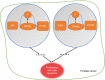
Results: PPP5C was highly expressed in PCa tissue as analyzed by immunohistochemistry and ONCOMINE datasets. PPP5C Knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and colony formation in PCa cells. Flow cytometry analysis showed that DU145, PC3 and 22RV1 PCa cells deprived of PPP5C were arrested in G0/G1 phase and became apoptotic. Western blot analysis indicated that PPP5C knockdown could promote JNK and ERK phosphorylation.
Conclusion: Our study indicated that the PPP5C may become a new potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for the PCa.
Keywords: ERK; JNK; PPP5C; prostate cancer; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Molitierno J, Evans A, Mohler JL, et al. Characterization of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Urol Int. 2006;77(2):130–134. - PubMed
-
- Roehl KA, Han M, Ramos CG, Antenor JA, Catalona WJ. Cancer progression and survival rates following anatomical radical retropubic prostatectomy in 3,478 consecutive patients: long-term results. J Urol. 2004;172(3):910–914. - PubMed
-
- Sharifi N, Gulley JL, Dahut WL. Androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. JAMA. 2005;294(2):238–244. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

