Acute pediatric hyperammonemia: current diagnosis and management strategies
- PMID: 30254497
- PMCID: PMC6140721
- DOI: 10.2147/HMER.S140711
Acute pediatric hyperammonemia: current diagnosis and management strategies
Abstract
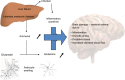
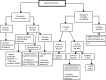
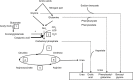
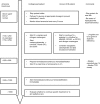
Acute hyperammonemia may induce a neurologic impairment leading to an acute life-threatening condition. Coma duration, ammonia peak level, and hyperammonemia duration are the main risk factors of hyperammonemia-related neurologic deficits and death. In children, hyperammonemia is mainly caused by severe liver failure and inborn errors of metabolism. In an acute setting, obtaining reliable plasma ammonia levels can be challenging because of the preanalytical difficulties that need to be addressed carefully. The management of hyperammonemia includes 1) identification of precipitating factors and cerebral edema presence, 2) a decrease in ammonia production by reducing protein intake and reversing catabolism, and 3) ammonia removal with pharmacologic treatment and, in the most severe cases, with extracorporeal therapies. In case of severe coma, transcranial Doppler ultrasound could be the method of choice to noninvasively monitor cerebral blood flow and titrate therapies.
Keywords: critical care; hemodialysis; hyperammonemia; pediatrics; sodium benzoate; sodium phenylacetate.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure P. Jouvet has received financial support from the Fonds de Recherche Santé Québec and from the Quebec Ministry of Health as well as from Sainte-Justine University Hospital. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Ozanne B, Nelson J, Cousineau J, et al. Threshold for toxicity from hyperammonemia in critically ill children. J Hepatol. 2012;56(1):123–128. - PubMed
-
- Hakvoort TB, He Y, Kulik W, et al. Pivotal role of glutamine synthetase in ammonia detoxification. Hepatology. 2017;65(1):281–293. - PubMed
-
- Auron A, Brophy PD. Hyperammonemia in review: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27(2):207–222. - PubMed
-
- Wijdicks EF. Hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(17):1660–1670. - PubMed
-
- Paprocka J, Jamroz E. Hyperammonemia in children: on the crossroad of different disorders. Neurologist. 2012;18(5):261–265. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

