Dynamic DNA Methylation Changes of Tbx21 and Rorc during Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis in Mice
- PMID: 30254507
- PMCID: PMC6142759
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9129163
Dynamic DNA Methylation Changes of Tbx21 and Rorc during Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis in Mice
Abstract
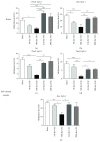
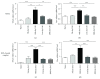
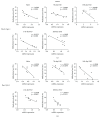
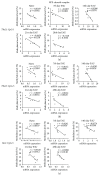
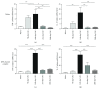
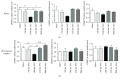
The key transcription factors of T helper cell subpopulations, including T-bet, GATA3, RORγt, and Foxp3 are involved in various autoimmune diseases. Whether methylation of these master transcription factors is associated with the development of experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) and the possible epigenetic regulatory mechanisms involved has however not yet been addressed. In our study, significant methylation changes in both Tbx21 and Rorc were observed in one CpG site in the retinas of EAU mice. Two CpG sites of Tbx21 and one CpG site of Rorc showed significant dynamic methylation changes in the RPE-choroid complex during EAU. The mRNA expressions of Tbx21 and Rorc in both the retinas and RPE-choroid complexes correlated with the methylation changes at the various time points during EAU development. The methylation changes were associated with the production of the Th1/Th17 cells' signature cytokines, IFN-γ and IL-17. Dynamic changes in mRNA expression of DNA methyltransferases (DNMT1) were also noted, which may be related to the observed methylation changes of these genes. The present study provides evidence that DNA methylation of Tbx21 and Rorc may be associated with the development of EAU. DNMT1 activation may have an important effect on regulating DNA methylation dynamics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TMP778, a selective inhibitor of RORγt, suppresses experimental autoimmune uveitis development, but affects both Th17 and Th1 cell populations.Eur J Immunol. 2018 Nov;48(11):1810-1816. doi: 10.1002/eji.201747029. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Eur J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30218573 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acids Suppress Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis in Association with Inhibition of Th1 and Th17 Cell Function.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 22;10(9):e0138241. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138241. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26393358 Free PMC article.
-
Copy number variants and genetic polymorphisms in TBX21, GATA3, Rorc, Foxp3 and susceptibility to Behcet's disease and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome.Sci Rep. 2015 Apr 15;5:9511. doi: 10.1038/srep09511. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25873156 Free PMC article.
-
Possible Role of the RORC Gene in Primary and Secondary Lymphedema: Review of the Literature and Genetic Study of Two Rare Causative Variants.Lymphat Res Biol. 2021 Apr;19(2):129-133. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2020.0030. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Lymphat Res Biol. 2021. PMID: 32960152 Review.
-
Combating Autoimmune Diseases With Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor-γ (RORγ or RORc) Inhibitors: Hits and Misses.J Med Chem. 2018 Dec 27;61(24):10976-10995. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00588. Epub 2018 Jul 30. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30010338 Review.
Cited by
-
Do epigenetic changes caused by commensal microbiota contribute to development of ocular disease? A review of evidence.Hum Genomics. 2020 Mar 13;14(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40246-020-00257-5. Hum Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32169120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-Molecule DNA Methylation Reveals Unique Epigenetic Identity Profiles of T Helper Cells.J Immunol. 2024 Mar 15;212(6):1029-1039. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300091. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38284984 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Mechanisms of the Ferroptosis-Related Gene TGFBR1 in Autoimmune Uveitis Based on Machine Learning Models.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 23;10(26):27830-27846. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00595. eCollection 2025 Jul 8. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40657117 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Analysis of Aqueous Humor Identifies Aberrant Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Metabolism in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada and Behcet's Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 22;12:587393. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.587393. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33732231 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of gut microbiota on eye diseases: an overview.Ann Med. 2021 Dec;53(1):750-761. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1925150. Ann Med. 2021. PMID: 34042554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nussenblatt R. B. Proctor lecture. Experimental autoimmune uveitis: mechanisms of disease and clinical therapeutic indications. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 1991;32(13):3131–3141. - PubMed
-
- Caspi R. R., Roberge F. G., Chan C. C., et al. A new model of autoimmune disease. Experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis induced in mice with two different retinal antigens. Journal of Immunology. 1988;140(5):1490–1495. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H. R., Lumsden L., Forrester J. V. Macrophages and dendritic cells in IRBP-induced experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in B10RIII mice. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 1999;40(13):3177–3185. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

