Laparoscopic technique of para-aortic lymph node dissection: A comparison of the different approaches to trans- versus extraperitoneal para-aortic lymphadenectomy
- PMID: 30254875
- PMCID: PMC6113969
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gmit.2016.01.003
Laparoscopic technique of para-aortic lymph node dissection: A comparison of the different approaches to trans- versus extraperitoneal para-aortic lymphadenectomy
Abstract
Since Dr Dargent first reported endoscopic surgery using retroperitoneal pelvicoscopy to perform pelvic lymph node sampling in 1987, many literature reviews on the safety and feasibility of laparoscopic staging surgery of gynecologic malignancies have been published. However, the procedure of laparoscopic lymphadenectomy is more difficult to perform due to the limited surgical space and associated technical problems. Especially in the para-aortic lymphadenectomy procedure, there are many barriers to overcome in the surgical field, learning curve, and technique. We present a review of lymphadenectomy, especially para-aortic lymphadenectomy.
Keywords: extraperitoneal; para-aortic lymphadenectomy; transperitoneal.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures
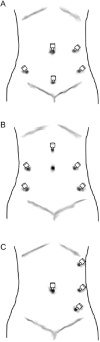

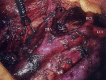
References
-
- Dargent D. A new future for Schauta's operation through presurgical retroperitoneal pelviscopy. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 1987;8:292–296.
-
- Querleu D, Leblanc E, Castelain B. Laparoscopic pelvic lymphadenectomy in the staging of early carcinoma of the cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991;164:579–581. - PubMed
-
- Childers JM, Hatch K, Surwit EA. The role of laparoscopic lymphadenectomy in the management of cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1992;47:38–43. - PubMed
-
- Childers JM, Hatch KD, Tran AN, Surwit EA. Laparoscopic para-aortic lymphadenectomy in gynecologic malignancies. Obstet Gynecol. 1993;82:741–747. - PubMed
-
- Nezhat CR, Nezhat FR, Burrell MO, et al. Laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and laparoscopically assisted vaginal radical hysterectomy with pelvic and paraaortic node dissection. J Gynecol Surg. 1993;9:105–120. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
