Prognostic Genes of Breast Cancer Identified by Gene Co-expression Network Analysis
- PMID: 30254986
- PMCID: PMC6141856
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00374
Prognostic Genes of Breast Cancer Identified by Gene Co-expression Network Analysis
Abstract
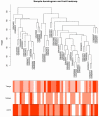
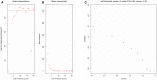
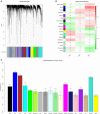
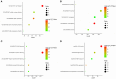
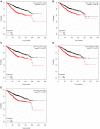
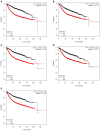
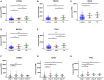
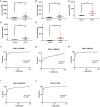
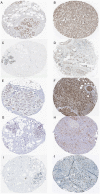
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies. The molecular mechanisms of its pathogenesis are still to be investigated. The aim of this study was to identify the potential genes associated with the progression of breast cancer. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was used to construct free-scale gene co-expression networks to explore the associations between gene sets and clinical features, and to identify candidate biomarkers. The gene expression profiles of GSE1561 were selected from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. RNA-seq data and clinical information of breast cancer from TCGA were used for validation. A total of 18 modules were identified via the average linkage hierarchical clustering. In the significant module (R2 = 0.48), 42 network hub genes were identified. Based on the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data, 5 hub genes (CCNB2, FBXO5, KIF4A, MCM10, and TPX2) were correlated with poor prognosis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve validated that the mRNA levels of these 5 genes exhibited excellent diagnostic efficiency for normal and tumor tissues. In addition, the protein levels of these 5 genes were also significantly higher in tumor tissues compared with normal tissues. Among them, CCNB2, KIF4A, and TPX2 were further upregulated in advanced tumor stage. In conclusion, 5 candidate biomarkers were identified for further basic and clinical research on breast cancer with co-expression network analysis.
Keywords: GEO; TCGA; breast cancer; prognosis; weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA).
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

