Hepatic damage associated with fatal zinc phosphide poisoning in broiler chicks
- PMID: 30255033
- PMCID: PMC6149249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijvsm.2016.10.002
Hepatic damage associated with fatal zinc phosphide poisoning in broiler chicks
Abstract
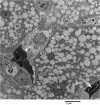
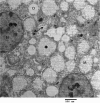
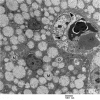
Zinc phosphide (Zn3P2) is a widely used rodenticide which has the potential to cause high mortality if ingested. The present study was designed in order to explore the hepatic injury in broiler chicks that were acutely intoxicated with Zn3P2. For this purpose, a total number of 12 broiler Saso chicks were divided into two equal groups. Birds of the first group were exposed to 300 ppm Zn3P2 via food. Hepatic damage of intoxicated birds was evaluated biochemically and histologically using the transmission electron microscope and subsequently compared with another healthy non-treated controls (second group). The serum activity of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) was significantly higher in those poisoned with Zn3P2, While, activities of both Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), as well as, zinc concentration of hepatic tissue did not represented a significant difference between treated and control birds. Histological examination revealed presence of numerous heterogenic shaped mitochondria in hepatocytes of non-treated birds. Glycogen deposits were also scattered in the form of large electron dense deposits. Kupffer cell was irregular in shape and had numerous pseudopods often projected into sinusoidal lumen. In hepatic cells of intoxicated birds, mitochondrial swelling with cristolysis, few glycogen deposits, vacuoles in the cytoplasm and shrunken darkly stained nuclei are the major ultra-structural changes which were detected. It was concluded that the mitochondria could be one of the main target in hepatocytes for the toxic effect of Zn3P2 in broiler chicks.
Keywords: Chicks; Electron microscope; Liver; Zinc phosphide.
Figures


References
-
- Osweiler G.D., Carson T.L., Buck W.B., Van Gelder G.A. 3rd ed. Kendnall/Hunt Publishing Co.; Dubuque, IA: 1985. Clinical and diagnostic veterinary toxicology.
-
- Casteel S.W., Bailey E.M. A review of zinc phosphide poisoning. J Vet Hum Toxicol. 1986;28:151–154. - PubMed
-
- Poppenga R.H., Ziegler A.F., Habecker P.L., Singletary D.L., Walter M.K., Miller P.G. Zinc phosphide intoxication of wild turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo) J Wildl Dis. 2005;41:218–223. - PubMed
-
- Bumbrah G.S., Krishan K., Kanchan T., Sharma M., Sodhi G.S. Phosphide poisoning: review of literature. Forensic Sci Int. 2012;214:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Tiwary A.K., Puschner B., Charlton B.R., Filigernzi M.S. Diagnosis of zinc phosphide poisoning in chickens using a new analytical approach. Avian Dis. 2005;49:288–291. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

