Determination of baseline bone mineral density using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in Suffolk-Dorset hybrid ewes
- PMID: 30255047
- PMCID: PMC6137841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijvsm.2017.03.001
Determination of baseline bone mineral density using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in Suffolk-Dorset hybrid ewes
Abstract
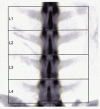
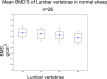
Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) has the ability to rapidly and non-invasively measure bone mineral density and is the most widely accepted method for quantitative assessment of bone mineral status in vivo. There is scarce information available on the baseline bone mineral density (BMD) values in adult intact Suffolk Dorset ewes (5-7 years), a frequently used animal model for the study of post-menopausal osteoporosis. The objective of the present study was to determine the baseline bone mineral density values in 26 adult intact Suffolk-Dorset hybrid ewes using a Lunar Prodigy DPX x-ray bone densitometer. The DEXA scans of the femur, lumbar spine (L3-L6) and calcaneus were obtained. Because of the low variability between the scans for the lumbar vertebrae and calcaneus in the first two animals, only two scans were obtained for the remaining animals of the study. The femoral scans were rejected due to high variability between the scans. The BMD was calculated using the standard GE antero-posterior human spine acquisition software. The bone mineral densities of regions of interest (ROIs) were compared by the Bonferroni significant difference technique. The results of the study demonstrated that the BMD progressively reduced from L3 to L6 and a strong correlation was found between the BMD values for the ROIs from L3 to L6. The present study provided a precise and rapid method for measuring the BMD of the lumbar spine in Suffolk-Dorset breed of sheep and recorded reference values in adult sheep.
Keywords: Bone mineral density; DEXA; Lumbar spine; Region of interest; Sheep.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in sheep: experiences with in vivo and ex vivo studies.Bone. 1995 Oct;17(4 Suppl):381S-387S. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(95)00315-5. Bone. 1995. PMID: 8579941
-
The effect of region of interest selection on dual energy X-ray absorptiometry measurements of the calcaneus in 55 post-menopausal women.Br J Radiol. 1999 Sep;72(861):864-71. doi: 10.1259/bjr.72.861.10645192. Br J Radiol. 1999. PMID: 10645192 Clinical Trial.
-
Lumbar computed tomography scans are not appropriate surrogates for bone mineral density scans in primary adult spinal deformity.Neurosurg Focus. 2017 Dec;43(6):E4. doi: 10.3171/2017.9.FOCUS17476. Neurosurg Focus. 2017. PMID: 29191096
-
Regional bone mineral density differences measured by quantitative computed tomography: does the standard clinically used L1-L2 average correlate with the entire lumbosacral spine?Spine J. 2019 Apr;19(4):695-702. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.10.007. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Spine J. 2019. PMID: 30343044
-
Calcaneus as a site for assessment of bone mineral density: evaluation in cadavers and healthy volunteers.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993 Sep;161(3):621-7. doi: 10.2214/ajr.161.3.8352120. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993. PMID: 8352120
References
-
- Blake G.M., Fogelman I. Applications of bone densitometry for osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1998;27(2):267–288. - PubMed
-
- Kanis J.A., Delmas P., Burckhardt P., Cooper C., Torgerson D.O. Guidelines for diagnosis and management of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 1997;7(4):390–406. - PubMed
-
- Watts N.B., Lewiecki E.M., Miller P.D., Baim S. National Osteoporosis Foundation 2008 Clinician's Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis and the World Health Organization Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX): what they mean to the bone densitometrist and bone technologist. J Clin Densitom. 2008;11(4):473–477. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, WHO scientific group on the assessment of osteoporosis at primary health care level, 2011.
-
- Grier S.J., Turner A.S., Alvis M.R. The use of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in animals. Invest Radiol. 1996;31(1):50–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

