Oxidative stress changes observed in selected organs of African giant rats (Cricetomys gambianus) exposed to sodium metavanadate
- PMID: 30255083
- PMCID: PMC6147385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijvsm.2018.03.004
Oxidative stress changes observed in selected organs of African giant rats (Cricetomys gambianus) exposed to sodium metavanadate
Abstract
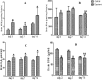
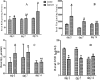
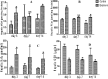
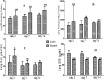
Vanadium is a contaminant of crude oil that released into the atmosphere through burning of fossil fuels. The mechanism by which it exerts toxic influences had not been fully elucidated in African giant rat (AGR). This study investigates the mechanisms of sodium metavanadate (SMV) induced oxidative stress in AGR. A total of 24 adult male AGR weighing 600-850 g were used. Animals were randomly divided into six groups. Groups 1, 3 and 5 served as control while groups 2, 4 and 6 were treated with intraperitoneal 3 mg/kg body weight of SMV for 3, 7 and 14 days, respectively. Serum, brain, liver, testes, kidneys, spleen and lungs were harvested for biochemical assays. SMV induced significant increase in malondialdehyde, hydrogen peroxide, sulfhydryl (total thiol) and protein carbonyl levels but decreased non-protein thiol levels in tissues accessed. A significant decrease was observed in glutathione-S-transferase (GST), superoxide dismutase (SOD), reduced glutathione (GSH) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) levels in SMV treated rats compared to controls. Serum myeloperoxidase, xanthine oxidase and Advanced Oxidative Protein Products (AOPP) were markedly increased while nitrous oxide levels were significantly decreased in all treated groups. SMV exposure to AGR induced oxidative stress through generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and depletion of the antioxidant defence system. These conditions could become severe with prolonged exposure.
Keywords: Air-pollution; Glutathione; Oxidative-stress; Protein carbonyl; Sulfhydryl; Vanadium.
Figures


References
-
- Igado O.O., Olopade J.O., Onwuka S.K., Chukwudi A.C., Daramola O.A., Ajufo U.E. Evidence of Environmental Pollution in caprine brains obtained from a Relatively Unindustrialized Area in Nigeria. Afr J Biomed Res. 2008;11:305–309.
-
- Olopade J.O., Onwuka S.K., Adejumo D., Ladokun A.A. Analysis of some industrial metals and ions in the cerebral cortex of goats in Nigeria. Nig Vet J. 2005;26:51–55.
-
- Calderon-Garciduenas L., Maronpot R.R., Torres-Jardon R., Henriquez-Roldan C., Schoonhoven R., Acuna-Ayala H. DNA damage in nasal and brain tissues of canines exposed to air pollution is associated with evidence of chronic brain inflammation and neurodegeneration. Toxicol Pathol. 2003;31:524–538. - PubMed
-
- Usende I.L., Leitner D.F., Neely E., Connor J.R., Olopade J.O. The deterioration seen in myelin related morpho-physiology in vanadium exposed rats is partially protected by concurrent iron deficiency. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2016;31:11–22. - PubMed
-
- Domingo J.L. Developmental Toxicity of Metal Chelating Agents. Reprod Toxicol Rev. 1998;12:499–500. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

