A Prospective Observational Study of Hypogammaglobulinemia in the First Year After Lung Transplantation
- PMID: 30255132
- PMCID: PMC6092181
- DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000000811
A Prospective Observational Study of Hypogammaglobulinemia in the First Year After Lung Transplantation
Abstract
Background: Immunosuppressive therapies have led to improved survival for lung transplant (LT) recipients but these therapies can lead to hypogammaglobulinemia (HGG) and potentially an increased risk of infection. Large prospective studies have not been performed to evaluate the impact of HGG on outcomes for LT recipients.
Methods: This is a single-center prospective observational study of LT recipients. Pretransplant and posttransplant IgG levels were measured and related to infection, rejection, antibiotic use, and immunosuppression use.
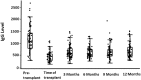
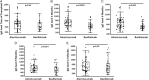
Results: One hundred thirty-three LT recipients were prospectively evaluated. Pretransplant IgG values were higher than IgG values at the time of transplant or any time thereafter (all P < 0.0001). Severe HGG (IgG < 400 mg/dL) was highest at the time of transplant (32.4%) while at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months posttransplant the prevalence of severe HGG was 7.4%, 7.5%, 8.9%, and 6.3%, respectively. Severe HGG was associated with 2 or more pneumonias (P = 0.0006) and increased number of antibiotic courses (P = 0.003) compared with the subjects without severe HGG. Pretransplant IgG level and less than 30% of pretransplant protective pneumococcal antibody levels were identified as pretransplant risk factors for severe HGG. In multivariate analysis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease as the underlying disease and the use of basiliximab as the induction agent in conjunction with higher prednisone and mycophenolate dosing were most predictive of severe HGG (P = 0.005), whereas the combination of age, severe HGG and number of acute steroid courses were most predictive of total days of pneumonia (P = 0.0001).
Conclusions: Our large prospective study identifies risk factors for severe HGG after LT and demonstrates that LT recipients with severe HGG are at increased risk for recurrent pneumonias and more antibiotic courses.
Figures



References
-
- Orange JS, Hossny EM, Weiler CR, et al. Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in human disease: a review of evidence by members of the Primary Immunodeficiency Committee of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:S525–S553. - PubMed
-
- Bonilla FA, Khan DA, Ballas ZK, et al. Practice parameter for the diagnosis and management of primary immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:1186–1205. - PubMed
-
- Dhalla F, Misbah SA. Secondary antibody deficiencies. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;15:505–513. - PubMed
-
- Yusen RD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-second official adult lung and heart-lung transplantation report—2015; focus theme: early graft failure. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015;34:1264–1277. - PubMed
-
- Florescu DF, Kalil AC, Qiu F, et al. What is the impact of hypogammaglobulinemia on the rate of infections and survival in solid organ transplantation? A meta-analysis. Am J Transplant. 2013;13:2601–2610. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

