Illuminating the Activated Brain: Emerging Activity-Dependent Tools to Capture and Control Functional Neural Circuits
- PMID: 30255458
- PMCID: PMC6527722
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-018-0291-x
Illuminating the Activated Brain: Emerging Activity-Dependent Tools to Capture and Control Functional Neural Circuits
Abstract
Immediate-early genes (IEGs) have long been used to visualize neural activations induced by sensory and behavioral stimuli. Recent advances in imaging techniques have made it possible to use endogenous IEG signals to visualize and discriminate neural ensembles activated by multiple stimuli, and to map whole-brain-scale neural activation at single-neuron resolution. In addition, a collection of IEG-dependent molecular tools has been developed that can be used to complement the labeling of endogenous IEG genes and, especially, to manipulate activated neural ensembles in order to reveal the circuits and mechanisms underlying different behaviors. Here, we review these techniques and tools in terms of their utility in studying functional neural circuits. In addition, we provide an experimental strategy to measure the signal-to-noise ratio of IEG-dependent molecular tools, for evaluating their suitability for investigating relevant circuits and behaviors.
Keywords: Activity-dependent tools; Arc; Emotion; Immediate-early gene; Neural ensembles; c-fos.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors claim that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


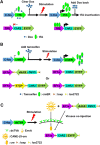
References
-
- Hu H. Reward and aversion. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2016;39:297–324. - PubMed
-
- Cole AJ, Saffen DW, Baraban JM, Worley PF. Rapid increase of an immediate early gene messenger RNA in hippocampal neurons by synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Nature. 1989;340:474–476. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP, Sheng M, Lau LF, Greenberg ME. Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Genes Dev. 1989;3:304–313. - PubMed
-
- Morgan JI, Cohen DR, Hempstead JL, Curran T. Mapping patterns of c-fos expression in the central nervous system after seizure. Science. 1987;237:192–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

