SiRNA silencing efficacy prediction based on a deep architecture
- PMID: 30255786
- PMCID: PMC6157246
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-5028-8
SiRNA silencing efficacy prediction based on a deep architecture
Abstract
Background: Small interfering RNA (siRNA) can be used to post-transcriptional gene regulation by knocking down targeted genes. In functional genomics, biomedical research and cancer therapeutics, siRNA design is a critical research topic. Various computational algorithms have been developed to select the most effective siRNA, whereas the efficacy prediction accuracy is not so satisfactory. Many existing computational methods are based on feature engineering, which may lead to biased and incomplete features. Deep learning utilizes non-linear mapping operations to detect potential feature pattern and has been considered perform better than existing machine learning method.
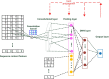
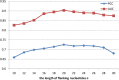
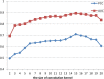
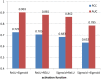
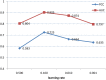
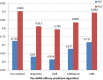
Results: In this paper, to further improve the prediction accuracy and facilitate gene functional studies, we developed a new powerful siRNA efficacy predictor based on a deep architecture. First, we extracted hidden feature patterns from two modalities, including sequence context features and thermodynamic property. Then, we constructed a deep architecture to implement the prediction. On the available largest siRNA database, the performance of our proposed method was measured with 0.725 PCC and 0.903 AUC value. The comparative experiment showed that our proposed architecture outperformed several siRNA prediction methods.
Conclusions: The results demonstrate that our deep architecture is stable and efficient to predict siRNA silencing efficacy. The method could help select candidate siRNA for targeted mRNA, and further promote the development of RNA interference.
Keywords: Deep learning; RNAi; siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
The authors consent to publish this paper to BMC Genomics.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
siRNADiscovery: a graph neural network for siRNA efficacy prediction via deep RNA sequence analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Sep 23;25(6):bbae563. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae563. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39503523 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient prediction methods for selecting effective siRNA sequences.Comput Biol Med. 2010 Feb;40(2):149-58. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2009.11.011. Comput Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20022002
-
Predicting siRNA efficacy based on multiple selective siRNA representations and their combination at score level.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 20;7:44836. doi: 10.1038/srep44836. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28317874 Free PMC article.
-
Precise and efficient siRNA design: a key point in competent gene silencing.Cancer Gene Ther. 2016 Apr;23(4):73-82. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2016.4. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016. PMID: 26987292 Review.
-
Hydrophobization and bioconjugation for enhanced siRNA delivery and targeting.RNA. 2007 Apr;13(4):431-56. doi: 10.1261/rna.459807. Epub 2007 Feb 28. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17329355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assembling the RNA therapeutics toolbox.Med Rev (2021). 2024 Mar 20;4(2):110-128. doi: 10.1515/mr-2023-0062. eCollection 2024 Apr. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 38680684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
siRNADiscovery: a graph neural network for siRNA efficacy prediction via deep RNA sequence analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Sep 23;25(6):bbae563. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae563. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39503523 Free PMC article.
-
A Graph Neural Network Approach for the Analysis of siRNA-Target Biological Networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 17;23(22):14211. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214211. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430688 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric trichotomous partitioning overcomes dataset limitations in building machine learning models for predicting siRNA efficacy.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Jun 14;33:93-109. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.06.010. eCollection 2023 Sep 12. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 37456778 Free PMC article.
-
Systematics for types and effects of RNA variations.RNA Biol. 2021 Apr;18(4):481-498. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1817266. Epub 2020 Sep 20. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 32951567 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

