Palladium-Catalyzed C(sp3 )-H Arylation of Primary Amines Using a Catalytic Alkyl Acetal to Form a Transient Directing Group
- PMID: 30255961
- PMCID: PMC6391947
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201804515
Palladium-Catalyzed C(sp3 )-H Arylation of Primary Amines Using a Catalytic Alkyl Acetal to Form a Transient Directing Group
Abstract
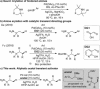
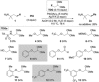
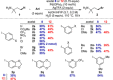
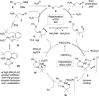
C-H Functionalization of amines is a prominent challenge due to the strong complexation of amines to transition metal catalysts, and therefore typically requires derivatization at nitrogen with a directing group. Transient directing groups (TDGs) permit C-H functionalization in a single operation, without needing these additional steps for directing group installation and removal. Here we report a palladium catalyzed γ-C-H arylation of amines using catalytic amounts of alkyl acetals as transient activators (e.g. commercially available (2,2-dimethoxyethoxy)benzene). This simple additive enables arylation of amines with a wide range of aryl iodides. Key structural features of the novel TDG are examined, demonstrating an important role for the masked carbonyl and ether functionalities. Detailed kinetic (RPKA) and mechanistic investigations determine the order in all reagents, and identify cyclopalladation as the turnover limiting step. Finally, the discovery of an unprecedented off-cycle free-amine directed ϵ-cyclopalladation of the arylation product is reported.
Keywords: C−H functionalization; amines; homogeneous catalysis; palladium; reaction kinetics.
© 2018 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Pd-Catalyzed γ-C(sp3)-H Arylation of Free Amines Using a Transient Directing Group.J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Nov 9;138(44):14554-14557. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b09653. Epub 2016 Nov 1. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 27786439 Free PMC article.
-
Palladium-Catalyzed β-C(sp3)-H Arylation of Aliphatic Ketones Enabled by a Transient Directing Group.J Org Chem. 2021 May 21;86(10):7296-7303. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c00646. Epub 2021 May 5. J Org Chem. 2021. PMID: 33950672
-
Amine-Catalyzed Copper-Mediated C-H Sulfonylation of Benzaldehydes via a Transient Imine Directing Group.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Jul 4;61(27):e202202933. doi: 10.1002/anie.202202933. Epub 2022 May 5. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 35441781 Free PMC article.
-
Free Amine, Hydroxyl and Sulfhydryl Directed C-H Functionalization and Annulation: Application to Heterocycle Synthesis.Chem Rec. 2022 Feb;22(2):e202100171. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202100171. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Chem Rec. 2022. PMID: 34436813 Review.
-
Transition Metal Catalyzed Free-Amine (-NH2 ) Directed C-H Bond Activation and Functionalization for Biaryl Frameworks.Chem Rec. 2021 Dec;21(12):3795-3817. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202100158. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Chem Rec. 2021. PMID: 34235831 Review.
Cited by
-
C-H Bond Functionalization of Amines: A Graphical Overview of Diverse Methods.SynOpen. 2021;5(3):173-228. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1706051. Epub 2021 Aug 12. SynOpen. 2021. PMID: 34825124 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Copper- and Aldehyde-Catalyzed Transient C-H Sulfonylation of Benzylamines.Org Lett. 2023 Jul 21;25(28):5285-5290. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.3c01783. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Org Lett. 2023. PMID: 37439636 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Directing Group Enabled Pd-catalyzed γ-C(sp3)-H Oxygenation of Alkyl Amines.ACS Catal. 2020 May 15;10(10):5657-5662. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c01310. Epub 2020 Apr 24. ACS Catal. 2020. PMID: 33996194 Free PMC article.
-
Pd-Catalyzed γ-C(sp3)-H Fluorination of Free Amines.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Jun 3;142(22):9966-9974. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b13537. Epub 2020 May 18. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32363869 Free PMC article.
-
Selective C-H Activation of Unprotected Allylamines by Control of Catalyst Speciation.Chem Catal. 2023 Nov 16;3(11):100809. doi: 10.1016/j.checat.2023.100809. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Chem Catal. 2023. PMID: 37982045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vitaku E., Smith D. T., Njardarson J. T., J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10257–10274. - PubMed
-
- None
-
- He J., Hamann L. G., Davies H. M. L., Beckwith R. E. J., Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5943; - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi J., Yamaguchi A. D., Itami K., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8960–9009; - PubMed
- Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 9092–9142.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

