Regression of Asymmetric Upper Extremity Tremor After Liver Transplantation in a Patient With Hepatic Encephalopathy: Case Report
- PMID: 30256030
- PMCID: PMC6400343
- DOI: 10.20471/acc.2018.57.01.25
Regression of Asymmetric Upper Extremity Tremor After Liver Transplantation in a Patient With Hepatic Encephalopathy: Case Report
Abstract
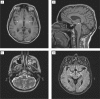
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a brain dysfunction caused by liver failure. Clinically, it can manifests as a wide spectrum of neurological or psychiatric abnormalities. This report presents a case of a 43-year-old male with HE and asymmetric kinetic, postural and resting tremor of upper extremities. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain showed signal abnormalities in numerous areas. The patient underwent liver transplantation and six months after normalization of liver function, tremor as well as brain MRI abnormalities almost completely regressed. This case re-port presents the asymmetric and reversible kinetic, postural and resting tremor of upper extremities as part of the spectrum of neurological abnormalities in HE.
Keywords: Case reports; Hepatic encephalopathy; Liver transplantation; Magnetic resonance imaging; Tremor.
Figures

References
-
- Cordoba J, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy. In: Schiff ER, Sorrell MF, Maddrey WC, eds. Schiff‘s Diseases of the Liver. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003: p 595-623.
-
- Cordoba J. Hepatic encephalopathy: from the pathogenesis to the new treatments –Review Article. ISRN Hepatology. 2014, Article ID 236268, 16 pages, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/236268 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adams RD, Foley JM. The neurological disorder associated with liver disease. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1953;32:198–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
