Pharmacokinetics and ex vivo anti-inflammatory effects of oral misoprostol in horses
- PMID: 30256450
- PMCID: PMC6587934
- DOI: 10.1111/evj.13024
Pharmacokinetics and ex vivo anti-inflammatory effects of oral misoprostol in horses
Abstract
Background: Misoprostol is an E prostanoid (EP) 2, 3 and 4 receptor agonist that is anecdotally used to treat and prevent NSAID-induced GI injury in horses. Misoprostol elicits anti-inflammatory effects in vivo in men and rodents, and inhibits TNFα production in equine leucocytes in vitro.
Objective: Define the pharmacokinetic parameters of oral misoprostol in horses, and determine the inhibitory effect of oral misoprostol administration on equine leucocyte TNFα production in an ex vivo inflammation model.
Study design: Pharmacokinetic study, ex vivo experimental study.
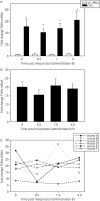
Methods: Six healthy adult horses of mixed breeds were used. In phase one, horses were given 5 μg/kg misoprostol orally, and blood was collected at predetermined times for determination of misoprostol free acid (MFA) by UHPLC-MS/MS. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated. In phase two, horses were dosed as in phase one, and blood was collected at T0, 0.5, 1 and 4 h following misoprostol administration for leucocyte isolation. Leucocytes were stimulated with 100 ng/mL LPS, and TNFα mRNA concentrations were determined via quantitative real-time PCR.
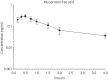
Results: About 5 μg/kg oral misoprostol produced a rapid time to maximum concentration (Tmax ) of 23.4 ± 2.4 min, with a maximum concentration (Cmax ) of 0.29 ± 0.07 ng/mL and area under the curve (AUC0-∞ ) of 0.4 ± 0.12 h ng/mL. LPS stimulation of equine leucocytes ex vivo significantly increased TNFα mRNA concentrations, and there was no significant effect of misoprostol even at the Tmax .
Main limitations: Only a single dose was used, and sample size was small.
Conclusions: Misoprostol is rapidly absorbed following oral administration in horses, and a single 5 μg/kg dose had no significant inhibitory effect on ex vivo LPS-stimulated TNFα mRNA production in leucocytes. Further studies analysing different dosing strategies, including repeat administration or combination with other anti-inflammatory drugs, are warranted.
Keywords: E prostanoid receptor agonist; horse; inflammation; leucocyte; pharmacokinetics; tumour necrosis factor-α.
© 2018 The Authors. Equine Veterinary Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of EVJ Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Morris, D.D. , Crowe, N. and Moore, J.N. (1990) Correlation of clinical and laboratory data with serum tumor necrosis factor activity in horses with experimentally induced endotoxemia. Am. J. Vet. Res. 51, 1935‐1940. - PubMed
-
- Kwon, S. , Moore, J.N. , Robertson, T.P. , Hurley, D.J. , Wagner, B. and Vandenplas, M.L. (2013) Disparate effects of LPS infusion and carbohydrate overload on inflammatory gene expression in equine laminae. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 155, 1‐8. - PubMed
-
- Strassheim, D. , Park, J.S. and Abraham, E. (2002) Sepsis: current concepts in intracellular signaling. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 34, 1527‐1533. - PubMed
-
- de la Rebiére de Pouyade, G. and Serteyn, D. (2011) The role of activated neutrophils in the early stage of equine laminitis. Vet. J. 189, 27‐33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

