A MATLAB toolbox for multivariate analysis of brain networks
- PMID: 30256496
- PMCID: PMC6289822
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24363
A MATLAB toolbox for multivariate analysis of brain networks
Abstract
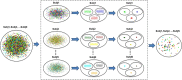
Complex brain networks formed via structural and functional interactions among brain regions are believed to underlie information processing and cognitive function. A growing number of studies indicate that altered brain network topology is associated with physiological, behavioral, and cognitive abnormalities. Graph theory is showing promise as a method for evaluating and explaining brain networks. However, multivariate frameworks that provide statistical inferences about how such networks relate to covariates of interest, such as disease phenotypes, in different study populations are yet to be developed. We have developed a freely available MATLAB toolbox with a graphical user interface that bridges this important gap between brain network analyses and statistical inference. The modeling framework implemented in this toolbox utilizes a mixed-effects multivariate regression framework that allows assessing brain network differences between study populations as well as assessing the effects of covariates of interest such as age, disease phenotype, and risk factors on the density and strength of brain connections in global (i.e., whole-brain) and local (i.e., subnetworks) brain networks. Confounding variables, such as sex, are controlled for through the implemented framework. A variety of neuroimaging data such as fMRI, EEG, and DTI can be analyzed with this toolbox, which makes it useful for a wide range of studies examining the structure and function of brain networks. The toolbox uses SAS, R, or Python (depending on software availability) to perform the statistical modeling. We also provide a clustering-based data reduction method that helps with model convergence and substantially reduces modeling time for large data sets.
Keywords: MATLAB toolbox; brain connections; brain networks; mixed-effects regression; multivariate modeling.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Bates, D. , Machler, M. , Bolker, B. M. , & Walker, S. C. (2015). Fitting linear mixed‐effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48.
-
- Bullmore, E. , & Sporns, O. (2009). Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(4), 186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

