Essential requirement of mammalian Pumilio family in embryonic development
- PMID: 30256721
- PMCID: PMC6329913
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E18-06-0369
Essential requirement of mammalian Pumilio family in embryonic development
Abstract
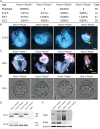
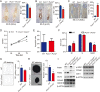
Mouse PUMILIO1 (PUM1) and PUMILIO2 (PUM2) belong to the PUF (Pumilio/FBF) family, a highly conserved RNA binding protein family whose homologues play critical roles in embryonic development and germ line stem cell maintenance in invertebrates. However, their roles in mammalian embryonic development and stem cell maintenance remained largely uncharacterized. Here we report an essential requirement of the Pum gene family in early embryonic development. A loss of both Pum1 and Pum2 genes led to gastrulation failure, resulting in embryo lethality at E8.5. Pum-deficient blastocysts, however, appeared morphologically normal, from which embryonic stem cells (ESCs) could be established. Both mutant ESCs and embryos exhibited reduced growth and increased expression of endoderm markers Gata6 and Lama1, making defects in growth and differentiation the likely causes of gastrulation failure. Furthermore, ESC Gata6 transcripts could be pulled down via PUM1 immunoprecipitation and mutation of conserved PUM-binding element on 3'UTR (untranslated region) of Gata6 enhanced the expression of luciferase reporter, implicating PUM-mediated posttranscriptional regulation of Gata6 expression in stem cell development and cell lineage determination. Hence, like its invertebrate homologues, mouse PUM proteins are conserved posttranscriptional regulators essential for embryonic and stem cell development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pumilio proteins utilize distinct regulatory mechanisms to achieve complementary functions required for pluripotency and embryogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 7;117(14):7851-7862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916471117. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32198202 Free PMC article.
-
Functions, mechanisms and regulation of Pumilio/Puf family RNA binding proteins: a comprehensive review.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jan;47(1):785-807. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05142-6. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 31643042 Review.
-
Loss of preimplantation embryo resulting from a Pum1 gene trap mutation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jun 19;462(1):8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.04.019. Epub 2015 Apr 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25896760
-
PUM1 and PUM2 exhibit different modes of regulation for SIAH1 that involve cooperativity with NANOS paralogues.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jan;76(1):147-161. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2926-5. Epub 2018 Sep 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30269240 Free PMC article.
-
The PUF family of RNA-binding proteins: does evolutionarily conserved structure equal conserved function?IUBMB Life. 2003 Jul;55(7):359-66. doi: 10.1080/15216540310001603093. IUBMB Life. 2003. PMID: 14584586 Review.
Cited by
-
The regulatory role of lncRNA in tumor drug resistance: refracting light through a narrow aperture.Oncol Res. 2025 Mar 19;33(4):837-849. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.053882. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40191723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian Pum1 and Pum2 Control Body Size via Translational Regulation of the Cell Cycle Inhibitor Cdkn1b.Cell Rep. 2019 Feb 26;26(9):2434-2450.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.111. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30811992 Free PMC article.
-
Pumilio proteins utilize distinct regulatory mechanisms to achieve complementary functions required for pluripotency and embryogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 7;117(14):7851-7862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916471117. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32198202 Free PMC article.
-
Functions, mechanisms and regulation of Pumilio/Puf family RNA binding proteins: a comprehensive review.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jan;47(1):785-807. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05142-6. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 31643042 Review.
-
Effects of PUMILIO1 and PUMILIO2 knockdown on cardiomyogenic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells culture.PLoS One. 2020 May 21;15(5):e0222373. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222373. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32437472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agami R. (2010). microRNAs, RNA binding proteins and cancer. Eur J Clin Invest , 370–374. - PubMed
-
- Crittenden SL, Bernstein DS, Bachorik JL, Thompson BE, Gallegos M, Petcherski AG, Moulder G, Barstead R, Wickens M, Kimble J. (2002). A conserved RNA-binding protein controls germline stem cells in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature , 660–663. - PubMed
-
- Day DA, Tuite MF. (1998). Post-transcriptional gene regulatory mechanisms in eukaryotes: an overview. J Endocrinol , 361–371. - PubMed
-
- Forbes A, Lehmann R. (1998). Nanos and Pumilio have critical roles in the development and function of germline stem cells. Development , 679–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

